Modulation of endothelial monolayer permeability induced by plasma obtained from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated whole blood
- PMID: 16634811
- PMCID: PMC1809663
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03074.x
Modulation of endothelial monolayer permeability induced by plasma obtained from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated whole blood
Abstract
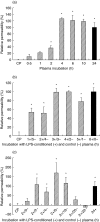
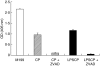
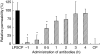
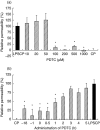
The aim of this study was to elucidate the time course of the permeability response of endothelial monolayers after exposure to plasma obtained from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated human whole blood; to investigate the role of apoptosis in monolayer permeability, and to inhibit the permeability increase, particularly after addition of the plasma stimulus. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were cultured on semiporous membranes and the permeability for albumin was measured after exposure, according to different schedules, to LPS-conditioned plasma. Apoptotic HUVEC were measured by both flow cytometry and ELISA. A variety of agents, including antibodies against cytokines, inhibitors of NF-kappaB, and a caspase inhibitor, were added to HUVEC, either prior to or after the stimulus. A maximum increase of the permeability was achieved after 4-6 h of exposure to LPS-conditioned plasma. This response was not accompanied by an increase in the number of apoptotic HUVEC. Administration of antibodies against both Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and Interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) to HUVEC within 1 h after stimulation significantly reduced the permeability increase. Similarly, pyrollidine di-thiocarbamate (PDTC), but not N-acetylcysteine, could prevent the permeability response, and was still effective when added within 2 h after LPS-conditioned plasma. The TNF-alpha/IL-1beta signal present in LPS-conditioned plasma appears to increase endothelial permeability through intracellular pathways that very likely involve the activation of NF-kappaB. Although poststimulatory inhibition of the permeability response proves to be possible with agents such as PDTC, the window of opportunity appears very small if placed in a clinical perspective.
Figures
References
-
- Aird WC. The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood. 2003;101:3765–77. - PubMed
-
- Bannerman DD, Goldblum SE. Direct effects of endotoxin on the endothelium. barrier function and injury. Laboratory Invest. 1999;79:1181–99. - PubMed
-
- Hull C, McLean G, Wong F, Duriez PJ, Karsan A. Lipopolysaccharide signals an endothelial apoptosis pathway through TNF receptor-associated factor 6-mediated activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Immunol. 2002;169:2611–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

