A neuropeptide Y Y5 antagonist selectively ameliorates body weight gain and associated parameters in diet-induced obese mice
- PMID: 16636293
- PMCID: PMC1459032
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0510320103
A neuropeptide Y Y5 antagonist selectively ameliorates body weight gain and associated parameters in diet-induced obese mice
Abstract
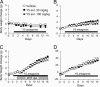
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is thought to have a major role in the physiological control of energy homeostasis. Among five NPY receptors described, the NPY Y5 receptor (Y5R) is a prime candidate to mediate some of the effects of NPY on energy homeostasis, although its role in physiologically relevant rodent obesity models remains poorly defined. We examined the effect of a potent and highly selective Y5R antagonist in rodent obesity and dietary models. The Y5R antagonist selectively ameliorated diet-induced obesity (DIO) in rodents by suppressing body weight gain and adiposity while improving the DIO-associated hyperinsulinemia. The compound did not affect the body weight of lean mice fed a regular diet or genetically obese leptin receptor-deficient mice or rats, despite similarly high brain Y5R receptor occupancy. The Y5R antagonist acts in a mechanism-based manner, as the compound did not affect DIO of Y5R-deficient mice. These results indicate that Y5R is involved in the regulation and development of DIO and suggest utility for Y5R antagonists in the treatment of obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

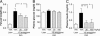


References
-
- Stanley B. G. In: The Biology of Neuropeptide Y and Related Peptides. Colmers W. F., Wahlestedt C., editors. Totowa, NJ: Humana; 1993. pp. 457–509.
-
- Beck B., Jhanwar-Uniyal M., Burlet A., Chapleur-Chateau M., Leibowitz S. F., Burlet C. Brain Res. 1990;528:245–249. - PubMed
-
- Sahu A., White J. D., Kalra P. S., Kalra S. P. Mol. Brain Res. 1992;15:15–18. - PubMed
-
- Stanley B. G., Kyrkouli S. E., Lampert S., Leibowitz S. F. Peptides. 1986;7:1189–1192. - PubMed
-
- Blomqvist A. G., Herzog H. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:294–298. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

