Ionic liquid-derived blood-compatible composite membranes for kidney dialysis
- PMID: 16637031
- PMCID: PMC4129660
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.30542
Ionic liquid-derived blood-compatible composite membranes for kidney dialysis
Abstract
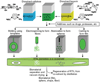
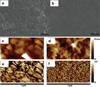
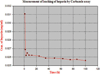
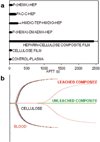
A novel heparin- and cellulose-based biocomposite is fabricated by exploiting the enhanced dissolution of polysaccharides in room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs). This represents the first reported example of using a new class of solvents, RTILs, to fabricate blood-compatible biomaterials. Using this approach, it is possible to fabricate the biomaterials in any form, such as films or membranes, fibers (nanometer- or micron-sized), spheres (nanometer- or micron-sized), or any shape using templates. In this work, we have evaluated a membrane film of this composite. Surface morphological studies on this biocomposite film showed the uniformly distributed presence of heparin throughout the cellulose matrix. Activated partial thromboplastin time and thromboelastography demonstrate that this composite is superior to other existing heparinized biomaterials in preventing clot formation in human blood plasma and in human whole blood. Membranes made of these composites allow the passage of urea while retaining albumin, representing a promising blood-compatible biomaterial for renal dialysis, with a possibility of eliminating the systemic administration of heparin to the patients undergoing renal dialysis.
(c) 2006 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Amass W, Amass A, Tighe B. A review of biodegrable polymers: Uses, current developments in the synthesis and characterization of biodegradable polyesters, blends of biodegradable polymers and recent advances in biodegradable studies. Polym Int. 1998;47:89–144.
-
- Langer R, Tirrell DA. Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature. 2004;428:487–492. - PubMed
-
- Modi GK, Pereira BJG, Jaber BL. Hemodialysis in acute renal failure : Does the membrane matter? Semin Dial. 2001;14:318–321. - PubMed
-
- Brieterman-White R. A review of heparin use in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. ANNA J. 1995;22:491–493. - PubMed
-
- Rydberg EJ, Westfall MJ, Nicholas RA. Low molecular weight heparin in preventing and treating DVT. Am Fam Physician. 1999;59:1607–1612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

