Neuroprotection from NMDA excitotoxic lesion by Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene delivery to the postnatal rat brain by a modular protein vector
- PMID: 16638118
- PMCID: PMC1462999
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-35
Neuroprotection from NMDA excitotoxic lesion by Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene delivery to the postnatal rat brain by a modular protein vector
Abstract
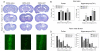
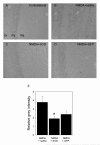
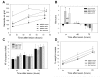
Background: Superoxide mediated oxidative stress is a key neuropathologic mechanism in acute central nervous system injuries. We have analyzed the neuroprotective efficacy of the transient overexpression of antioxidant enzyme Cu/Zn Superoxide dismutase (SOD) after excitotoxic injury to the immature rat brain by using a recently constructed modular protein vector for non-viral gene delivery termed NLSCt. For this purpose, animals were injected with the NLSCt vector carrying the Cu/Zn SOD or the control GFP transgenes 2 hours after intracortical N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) administration, and daily functional evaluation was performed. Moreover, 3 days after, lesion volume, neuronal degeneration and nitrotyrosine immunoreactivity were evaluated.
Results: Overexpression of Cu/Zn SOD transgene after NMDA administration showed improved functional outcome and a reduced lesion volume at 3 days post lesion. In secondary degenerative areas, increased neuronal survival as well as decreased numbers of degenerating neurons and nitrotyrosine immunoreactivity was seen. Interestingly, injection of the NLSCt vector carrying the control GFP transgene also displayed a significant neuroprotective effect but less pronounced.
Conclusion: When the appropriate levels of Cu/Zn SOD are expressed transiently after injury using the non-viral modular protein vector NLSCt a neuroprotective effect is seen. Thus recombinant modular protein vectors may be suitable for in vivo gene therapy, and Cu/Zn SOD should be considered as an interesting therapeutic transgene.
Figures
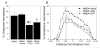
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-10 overexpression does not synergize with the neuroprotective action of RGD-containing vectors after postnatal brain excitotoxicity but modulates the main inflammatory cell responses.J Neurosci Res. 2012 Jan;90(1):143-59. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22741. Epub 2011 Sep 15. J Neurosci Res. 2012. PMID: 21922521
-
Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase expression in the postnatal rat brain following an excitotoxic injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2005 Jun 1;2(1):12. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-2-12. J Neuroinflammation. 2005. PMID: 15929797 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of impairment of cerebral blood flow autoregulation during acute stage of subarachnoid hemorrhage by gene transfer of Cu/Zn SOD-1 to cerebral vessels.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003 Jan;23(1):111-20. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000036561.60552.63. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003. PMID: 12500096
-
Zinc pre-treatment enhances NMDAR-mediated excitotoxicity in cultured cortical neurons from SOD1(G93A) mouse, a model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Jun;60(7-8):1200-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21056589
-
Lentiviral-mediated gene transfer of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is neuroprotective in a mouse model of neonatal excitotoxic challenge.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Jan;83(1):50-60. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20704. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16299771
Cited by
-
Engineering building blocks for self-assembling protein nanoparticles.Microb Cell Fact. 2010 Dec 30;9:101. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-9-101. Microb Cell Fact. 2010. PMID: 21192790 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of lentiviral vectors and modular protein nanovectors for traumatic brain injury gene therapy.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2014 Oct 15;1:14047. doi: 10.1038/mtm.2014.47. eCollection 2014. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2014. PMID: 26015985 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Radix Trichosanthis Saponins on Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:313657. doi: 10.1155/2015/313657. Epub 2015 May 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26089937 Free PMC article.
-
Nonviral approaches for neuronal delivery of nucleic acids.Pharm Res. 2008 May;25(5):983-98. doi: 10.1007/s11095-007-9439-5. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 17932730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
L-Norvaline, a new therapeutic agent against Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Sep;14(9):1562-1572. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.255980. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 31089055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McCord JM, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein) J Biol Chem. 1969;244:6049–6055. - PubMed
-
- DeKosky ST, Abrahamson EE, Taffe KM, Dixon CE, Kochanek PM, Ikonomovic MD. Effects of post-injury hypothermia and nerve growth factor infusion on antioxidant enzyme activity in the rat: implications for clinical therapies. J Neurochem. 2004;90:998–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02575.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

