Stable benzotriazole esters as mechanism-based inactivators of the severe acute respiratory syndrome 3CL protease
- PMID: 16638531
- PMCID: PMC7111201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2005.12.008
Stable benzotriazole esters as mechanism-based inactivators of the severe acute respiratory syndrome 3CL protease
Abstract
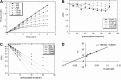
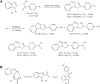
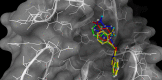
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is caused by a newly emerged coronavirus that infected more than 8000 individuals and resulted in more than 800 fatalities in 2003. Currently, there is no effective treatment for this epidemic. SARS-3CL(pro) has been shown to be essential for replication and is thus a target for drug discovery. Here, a class of stable benzotriazole esters was reported as mechanism-based inactivators of 3CL(pro), and the most potent inactivator exhibited a k(inact) of 0.0011 s(-1) and a K(i) of 7.5 nM. Mechanistic investigation with kinetic and mass spectrometry analyses indicates that the active site Cys145 is acylated, and that no irreversible inactivation was observed with the use of the C145A mutant. In addition, a noncovalent, competitive inhibition became apparent by using benzotriazole ester surrogates in which the bridged ester-oxygen group is replaced with carbon.
Figures



Comment in
-
Sometimes intermediates. Do the job!Chem Biol. 2006 Mar;13(3):235-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.03.002. Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 16638527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J.A., Lim W. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Drosten C., Günther S., Preiser W., van der Werf S., Brodt H.-R., Becker S., Rabenau H., Panning M., Kolesnikova L., Fouchier R.A.M. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Lee N., Hui D., Wu A., Chan P., Cameron P., Joynt G.M., Ahuja A., Yung M.Y., Leung C.B., To K.F. A major outbreak of severe acute respiration syndrome in Hong Kong. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1986–1994. - PubMed
-
- Poutanen S.M., Low D.E., Henry B., Finkelstein S., Rose D., Green K., Tellier R., Draker R., Adachi D., Ayers M.N. Canadian severe acute respiratory syndrome study, identification of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Canada. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1995–2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

