Hepatocyte growth factor mediates angiopoietin-induced smooth muscle cell recruitment
- PMID: 16638932
- PMCID: PMC1895873
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-09-012807
Hepatocyte growth factor mediates angiopoietin-induced smooth muscle cell recruitment
Abstract
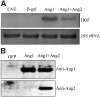
Communication between endothelial cells (ECs) and mural cells is critical in vascular maturation. Genetic studies suggest that angiopoietin/Tie2 signaling may play a role in the recruitment of pericytes or smooth muscle cells (SMCs) during vascular maturation. However, the molecular mechanism is unclear. We used microarray technology to analyze genes regulated by angiopoietin-1 (Ang1), an agonist ligand for Tie2, in endothelial cells (ECs). We observed that hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a mediator of mural cell motility, was up-regulated by Ang1 stimulation. We confirmed this finding by Northern blot and Western blot analyses in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Furthermore, stimulation of ECs with Ang1 increased SMC migration toward endothelial cells in a coculture assay. Addition of a neutralizing anti-HGF antibody inhibited Ang1-induced SMC recruitment, indicating that the induction of SMC migration by Ang1 was caused by the increase of HGF. Interestingly, Ang2, an antagonist ligand of Tie2, inhibited Ang1-induced HGF production and Ang1-induced SMC migration. Finally, we showed that deletion of Tie2 in transgenic mouse reduced HGF production. Collectively, our data reveal a novel mechanism of Ang/Tie2 signaling in regulating vascular maturation and suggest that a delicate balance between Ang1 and Ang2 is critical in this process.
Figures






References
-
- Hirschi KK, D'Amore PA. Pericytes in the microvasculature. Cardiovasc Res. 1996;32: 687-698. - PubMed
-
- Hungerford JE, Little CD. Developmental biology of the vascular smooth muscle cell: building a multilayered vessel wall. J Vasc Res. 1999;36: 2-27. - PubMed
-
- Armulik A, Abramsson A, Betsholtz C. Endothelial/pericyte interactions. Circ Res. 2005;97: 512-523. - PubMed
-
- Sato TN, Tozawa Y, Deutsch U, et al. Distinct roles of the receptor tyrosine kinases Tie-1 and Tie-2 in blood vessel formation. Nature. 1995; 376: 70-74. - PubMed
-
- Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, et al. Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science. 1997;277: 55-60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

