Reversal of Alzheimer's-like pathology and behavior in human APP transgenic mice by mutation of Asp664
- PMID: 16641106
- PMCID: PMC1459029
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0509695103
Reversal of Alzheimer's-like pathology and behavior in human APP transgenic mice by mutation of Asp664
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Apr 17;104(16):6876
Abstract
The deficits characteristic of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are believed to result, at least in part, from the neurotoxic effects of beta-amyloid peptides, a set of 39-43 amino acid fragments derived proteolytically from beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP). APP also is cleaved intracytoplasmically at Asp-664 to generate a second cytotoxic peptide, APP-C31, but whether this C-terminal processing of APP plays a role in the pathogenesis of AD is unknown. Therefore, we compared elements of the Alzheimer's phenotype in transgenic mice modeling AD with vs. without a functional Asp-664 caspase cleavage site. Surprisingly, whereas beta-amyloid production and plaque formation were unaltered, synaptic loss, astrogliosis, dentate gyral atrophy, increased neuronal precursor proliferation, and behavioral abnormalities were completely prevented by a mutation at Asp-664. These results suggest that Asp-664 plays a critical role in the generation of Alzheimer-related pathophysiological and behavioral changes in human APP transgenic mice, possibly as a cleavage site or via protein-protein interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
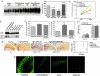
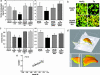

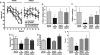
References
-
- Selkoe D. J. Science. 2002;298:789–791. - PubMed
-
- Gervais F. G., Xu D., Robertson G. S., Vaillancourt J. P., Zhu Y., Huang J., LeBlanc A., Smith D., Rigby M., Shearman M. S., et al. Cell. 1999;97:395–406. - PubMed
-
- Lu D. C., Rabizadeh S., Chandra S., Shayya R. F., Ellerby L. M., Ye X., Salvesen G. S., Koo E. H., Bredesen D. E. Nat. Med. 2000;6:397–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

