Human rhinovirus attenuates the type I interferon response by disrupting activation of interferon regulatory factor 3
- PMID: 16641293
- PMCID: PMC1472094
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.10.5021-5031.2006
Human rhinovirus attenuates the type I interferon response by disrupting activation of interferon regulatory factor 3
Erratum in
- J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(13):6722
Retraction in
-
Human rhinovirus attenuates the type I interferon response by disrupting activation of interferon regulatory factor 3.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):6161. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00433-07. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17496231 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
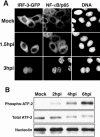
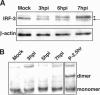
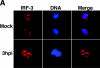
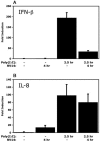
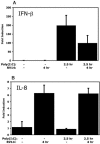
The type I interferon (IFN) response requires the coordinated activation of the latent transcription factors NF-kappaB, interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3), and ATF-2, which in turn activate transcription from the IFN-beta promoter. Synthesis and subsequent secretion of IFN-beta activate the Jak/STAT signaling pathway, resulting in the transcriptional induction of the full spectrum of antiviral gene products. We utilized high-density microarrays to examine the transcriptional response to rhinovirus type 14 (RV14) infection in HeLa cells, with particular emphasis on the type I interferon response and production of IFN-beta. We found that, although RV14 infection results in altered levels of a wide variety of host mRNAs, induction of IFN-beta mRNA or activation of the Jak/STAT pathway is not seen. Prior work has shown, and our results have confirmed, that NF-kappaB and ATF-2 are activated following infection. Since many viruses are known to target IRF-3 to inhibit the induction of IFN-beta mRNA, we analyzed the status of IRF-3 in infected cells. IRF-3 was translocated to the nucleus and phosphorylated in RV14-infected cells. Despite this apparent activation, very little homodimerization of IRF-3 was evident following infection. Similar results in A549 lung alveolar epithelial cells demonstrated the biological relevance of these findings to RV14 pathogenesis. In addition, prior infection of cells with RV14 prevented the induction of IFN-beta mRNA following treatment with double-stranded RNA, indicating that RV14 encodes an activity that specifically inhibits this innate host defense pathway. Collectively, these results indicate that RV14 infection inhibits the host type I interferon response by interfering with IRF-3 activation.
Figures



References
-
- Abzug, M. J., A. C. Beam, E. A. Gyorkos, and M. J. Levin. 1990. Viral pneumonia in the first month of life. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 9:881-885. - PubMed
-
- Bertino, J. S. 2002. Cost burden of viral respiratory infections: issues for formulary decision makers. Am. J. Med. 112(Suppl. 6A):42S-49S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

