Coverage and power in genomewide association studies
- PMID: 16642443
- PMCID: PMC1474045
- DOI: 10.1086/503751
Coverage and power in genomewide association studies
Abstract
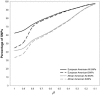
The ability of genomewide association studies to decipher genetic traits is driven in part by how well the measured single-nucleotide polymorphisms "cover" the unmeasured causal variants. Estimates of coverage based on standard linkage-disequilibrium measures, such as the average maximum squared correlation coefficient (r2), can lead to inaccurate and inflated estimates of the power of genomewide association studies. In contrast, use of the "cumulative r2 adjusted power" measure presented here gives more-accurate estimates of power for genomewide association studies.
Figures

References
Web Resources
-
- Quanto software, http://hydra.usc.edu/GxE/
References
-
- Risch N, Teng J (1998) The relative power of family-based and case-control designs for linkage disequilibrium studies of complex human diseases I. DNA pooling. Genome Res 8:1273–1288 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

