Differentiation of the roles of NO from airway epithelium and inflammatory cells in ozone-induced lung inflammation
- PMID: 16643973
- PMCID: PMC1594585
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.03.005
Differentiation of the roles of NO from airway epithelium and inflammatory cells in ozone-induced lung inflammation
Abstract
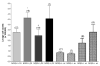
Mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2-/-) are more susceptible to ozone-induced lung inflammation and injury than their isogenic wild-type (NOS2+/+) counterparts, demonstrating an apparent protective effect for NOS2 in murine lungs. We hypothesized that nitric oxide (NO) generated from either NOS2 in the airway epithelial cells or the bone-marrow-derived inflammatory cells was responsible for the protective effect of NOS2. To test this hypothesis, we prepared chimeric mice by killing their endogenous bone marrow cells by whole body irradiation followed by bone marrow transplantation from a heterologous donor mouse. We exposed C57BL/6 (NOS2+/+), NOS2-/-, and chimeric NOS2 mice (NOS2-/+, NOS2+/-) to 1 ppm of ozone for 3 consecutive nights. NOS2-/- mice were more severely injured after exposure to ozone than C57BL/6 mice, including a more robust inflammatory cell influx (4.14 x 10(5) +/- 2.19 x 10(5) vs. 2.78 x 10(5) +/- 1.36 x 10(5) cells respectively; P = 0.036) and greater oxidation of total protein sulfhydryls (R-SH) in their blood plasma. Chimeric NOS2-/+ mice, which had bone marrow from NOS2-/- mice transplanted into C57BL/6 recipients, had a significantly greater response to ozone (increased numbers of neutrophils in lung lavage and decreased concentrations of exhaled NO) as compared to the reciprocal chimeric strain (NOS2+/-). We conclude that NOS2 has a protective effect against acute lung injury caused by ozone inhalation, which may be mediated, in part, by NO generated by NOS2 from inflammatory cells, predominantly neutrophils, recruited into the lung.
Figures

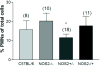




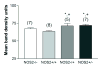

Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide synthase-2 down-regulates surfactant protein-B expression and enhances endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice.FASEB J. 2004 Aug;18(11):1276-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-1518fje. Epub 2004 Jun 18. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15208261
-
Toll-like receptor 4 mediates ozone-induced murine lung hyperpermeability via inducible nitric oxide synthase.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001 Feb;280(2):L326-33. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.2.L326. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11159012
-
Susceptibility to ozone-induced acute lung injury in iNOS-deficient mice.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002 Mar;282(3):L540-5. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00297.2001. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11839550
-
Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in ozone-induced lung injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;500:183-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0667-6_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001. PMID: 11764933 Review.
-
The Chemical Biology of NO that Regulates Oncogenic Signaling and Metabolism: NOS2 and Its Role in Inflammatory Disease.Crit Rev Oncog. 2023;28(1):27-45. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2023047302. Crit Rev Oncog. 2023. PMID: 37824385 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia attenuates effector-target cell interaction in the airway and pulmonary vascular compartment.Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 Nov;150(2):358-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03495.x. Epub 2007 Sep 24. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17892511 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship of the interleukin-6 -174 G>C gene polymorphism with oxidative stress markers in Turkish polycystic ovary syndrome patients.J Endocrinol Invest. 2008 Jul;31(7):624-9. doi: 10.1007/BF03345614. J Endocrinol Invest. 2008. PMID: 18787381
-
Neuroendocrine Regulation of Air Pollution Health Effects: Emerging Insights.Toxicol Sci. 2018 Jul 1;164(1):9-20. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy129. Toxicol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29846720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse lung inflammation after instillation of particulate matter collected from a working dairy barn.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 May 1;236(3):348-57. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.02.023. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19272399 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide synthase enzymes in the airways of mice exposed to ovalbumin: NOS2 expression is NOS3 dependent.Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:321061. doi: 10.1155/2010/321061. Epub 2010 Oct 5. Mediators Inflamm. 2010. PMID: 20953358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreadis AA, Hazen SL, Comhair SA, Erzurum SC. Oxidative and nitrosative events in asthma. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;35:213–225. - PubMed
-
- Beckman JS, Koppenol WH. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:C1424–1437. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya S, Ghosh S, Dasgupta B, Mazumder D, Roy S, Majumdar S. Chemokine-induced leishmanicidal activity in murine macrophages via the generation of nitric oxide. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:1704–1708. - PubMed
-
- Cueto R, Squadrito GL, Bermudez E, Pryor WA. Identification of heptanal and nonanal in bronchoalveolar lavage from rats exposed to low levels of ozone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;188:129–134. - PubMed
-
- Eiserich JP, Hristova M, Cross CE, Jones AD, Freeman BA, Halliwell B, van der Vliet A. Formation of nitric oxide-derived inflammatory oxidants by myeloperoxidase in neutrophils. Nature. 1998;391:393–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

