Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in the liver: a new strategy for the management of metabolic hepatic disorders
- PMID: 16644802
- PMCID: PMC1817784
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.108506
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in the liver: a new strategy for the management of metabolic hepatic disorders
Abstract
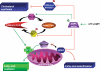
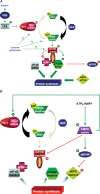
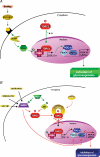
It is now becoming evident that the liver has an important role in the control of whole body metabolism of energy nutrients. In this review, we focus on recent findings showing that AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays a major role in the control of hepatic metabolism. AMPK integrates nutritional and hormonal signals to promote energy balance by switching on catabolic pathways and switching off ATP-consuming pathways, both by short-term effects on phosphorylation of regulatory proteins and by long-term effects on gene expression. Activation of AMPK in the liver leads to the stimulation of fatty acid oxidation and inhibition of lipogenesis, glucose production and protein synthesis. Medical interest in the AMPK system has recently increased with the demonstration that AMPK could mediate some of the effects of the fat cell-derived adiponectin and the antidiabetic drugs metformin and thiazolidinediones. These findings reinforce the idea that pharmacological activation of AMPK may provide, through signalling and metabolic and gene expression effects, a new strategy for the management of metabolic hepatic disorders linked to type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Figures
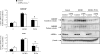
Similar articles
-
[Regulation of energy metabolism by AMPK: a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases].Med Sci (Paris). 2006 Apr;22(4):381-8. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2006224381. Med Sci (Paris). 2006. PMID: 16597407 Review. French.
-
Targeting AMP-activated protein kinase as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of metabolic disorders.Diabetes Metab. 2007 Dec;33(6):395-402. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2007.10.004. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Diabetes Metab. 2007. PMID: 17997341 Review.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling.Circ Res. 2007 Feb 16;100(3):328-41. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000256090.42690.05. Circ Res. 2007. PMID: 17307971 Review.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase and type 2 diabetes.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(5):583-9. doi: 10.2174/092986706776055724. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16515522 Review.
-
Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action.J Clin Invest. 2001 Oct;108(8):1167-74. doi: 10.1172/JCI13505. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11602624 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Acetic acid activates the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway to regulate lipid metabolism in bovine hepatocytes.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 4;8(7):e67880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067880. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861826 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms linking obesity, chronic kidney disease, and fatty liver disease: the roles of fetuin-A, adiponectin, and AMPK.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Mar;21(3):406-12. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009080820. Epub 2010 Feb 11. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20150538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 overexpression attenuates offspring metabolic and liver disorders as a result of maternal high-fat feeding.J Physiol. 2019 Jan;597(2):467-480. doi: 10.1113/JP276957. Epub 2018 Oct 31. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30381838 Free PMC article.
-
L-Arginine increases AMPK phosphorylation and the oxidation of energy substrates in hepatocytes, skeletal muscle cells, and adipocytes.Amino Acids. 2022 Dec;54(12):1553-1568. doi: 10.1007/s00726-022-03195-9. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Amino Acids. 2022. PMID: 35972552
-
Adiponectin protects against lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Mol Med Rep. 2018 May;17(5):7191-7201. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8748. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29568898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Elheiga L, Matzuk MM, Abo-Hashema KA, Wakil SJ. Continuous fatty acid oxidation and reduced fat storage in mice lacking acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2. Science. 2001;291:2613–2616. - PubMed
-
- Andreelli F, Foretz M, Knauf C, Cani PD, Perrin C, Iglesias MA, Pillot B, Bado A, Tronche F, Mithieux G, Vaulont S, Burcelin R, Viollet B. Liver adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase-α2 catalytic subunit is a key target for the control of hepatic glucose production by adiponectin and leptin but not by insulin. Endocrinology. 2006;147:2432–2441. - PubMed
-
- Assifi MM, Suchankova G, Constant S, Prentki M, Saha AK, Ruderman NB. AMP-activated protein kinase and coordination of hepatic fatty acid metabolism of starved/carbohydrate-refed rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005;289:E794–E800. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj M, Suraamornkul S, Pratipanawatr T, Hardies LJ, Pratipanawatr W, Glass L, Cersosimo E, Miyazaki Y, DeFronzo RA. Pioglitazone reduces hepatic fat content and augments splanchnic glucose uptake in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52:1364–1370. - PubMed
-
- Barthel A, Schmoll D, Kruger KD, Roth RA, Joost HG. Regulation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR (FOXO1a) by glucose starvation and AICAR, an activator of AMP-activated protein kinase. Endocrinology. 2002;143:3183–3186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

