The cation-chloride cotransporter NKCC1 promotes sharp waves in the neonatal rat hippocampus
- PMID: 16644806
- PMCID: PMC1779742
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.107086
The cation-chloride cotransporter NKCC1 promotes sharp waves in the neonatal rat hippocampus
Abstract
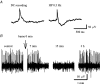
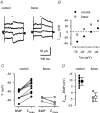
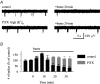
Earlier studies indicate a crucial role for the interconnected network of intrinsically bursting CA3 pyramidal neurons in the generation of in vivo hippocampal sharp waves (SPWs) and their proposed neonatal in vitro counterparts, the giant depolarizing potentials (GDPs). While mechanisms involving ligand- and voltage-gated channels have received lots of attention in the generation of CA3 network events in the immature hippocampus, the contribution of ion-transport mechanisms has not been extensively studied. Here, we show that bumetanide, a selective inhibitor of neuronal Cl- uptake mediated by the Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter isoform 1 (NKCC1), completely and reversibly blocks SPWs in the neonate (postnatal days 7-9) rat hippocampus in vivo, an action also seen on GDPs in slices (postnatal days 1-8). These findings strengthen the view that GDPs and early SPWs are homologous events. Gramicidin-perforated patch recordings indicated that NKCC1 accounts for a large ( approximately 10 mV) depolarizing driving force for the GABAA current in the immature CA3 pyramids. Consistent with a reduction in the depolarization mediated by endogenous GABAA-receptor activation, bumetanide inhibited the spontaneous bursts of individual neonatal CA3 pyramids, but it slightly increased the interneuronal activity as seen in the frequency of spontaneous GABAergic currents. An inhibitory effect of bumetanide was seen on the in vitro population events in the absence of synaptic GABAA receptor-mediated transmission, provided that a tonic GABAA receptor-mediated current was present. Our work indicates that NKCC1 expressed in CA3 pyramidal neurons promotes network activity in the developing hippocampus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Low expression of Kv7/M channels facilitates intrinsic and network bursting in the developing rat hippocampus.J Physiol. 2008 Nov 15;586(22):5437-53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.156257. Epub 2008 Sep 18. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18801845 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronization of GABAergic interneuronal network in CA3 subfield of neonatal rat hippocampal slices.J Physiol. 1997 Feb 1;498 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):763-72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp021900. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9051587 Free PMC article.
-
Compensatory enhancement of intrinsic spiking upon NKCC1 disruption in neonatal hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2009 May 27;29(21):6982-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0443-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19474325 Free PMC article.
-
The bumetanide-sensitive Na-K-2Cl cotransporter NKCC1 as a potential target of a novel mechanism-based treatment strategy for neonatal seizures.Neurosurg Focus. 2008 Sep;25(3):E22. doi: 10.3171/FOC/2008/25/9/E22. Neurosurg Focus. 2008. PMID: 18759624 Review.
-
Role of giant depolarizing potentials in shaping synaptic currents in the developing hippocampus.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):13-23. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.30. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725505 Review.
Cited by
-
NMDA receptors in GABAergic synapses during postnatal development.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037753. Epub 2012 May 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22662211 Free PMC article.
-
NKCC1 Deficiency in Forming Hippocampal Circuits Triggers Neurodevelopmental Disorder: Role of BDNF-TrkB Signalling.Brain Sci. 2022 Apr 15;12(4):502. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12040502. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35448033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A sensitive period of mice inhibitory system to neonatal GABA enhancement by vigabatrin is brain region dependent.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Apr;35(5):1138-54. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.219. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010. PMID: 20043003 Free PMC article.
-
Bumetanide for neonatal seizures: No light in the pharmacokinetic/dynamic tunnel.Epilepsia. 2022 Jul;63(7):1868-1873. doi: 10.1111/epi.17279. Epub 2022 May 26. Epilepsia. 2022. PMID: 35524446 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of GABAergic interneurons to the development of spontaneous activity patterns in cultured neocortical networks.Front Cell Neurosci. 2010 Jun 21;4:15. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2010.00015. eCollection 2010. Front Cell Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20617185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barry PH. JPCalc, a software package for calculating liquid junction potential corrections in patch-clamp, intracellular, epithelial and bilayer measurements and for correcting junction potential measurements. J Neurosci Meth. 1994;51:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Ben Ari Y. Developing networks play a similar melody. Trends Neurosci. 2001;24:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Bolea S, Avignone E, Berretta N, Sanchez-Andres JV, Cherubini E. Glutamate controls the induction of GABA-mediated giant depolarizing potentials through AMPA receptors in neonatal rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol. 1999;81:2095–2102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

