Validation of a novel ultra-short immunolabeling method for high-quality mRNA preservation in laser microdissection and real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
- PMID: 16645212
- PMCID: PMC1867592
- DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2006.050096
Validation of a novel ultra-short immunolabeling method for high-quality mRNA preservation in laser microdissection and real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction
Abstract
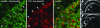
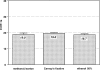
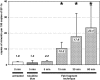
Laser microdissection allows isolation of tiny samples from tissue sections for analysis of gene expression by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Although immunohistochemical labeling is often required to identify target structures, it drastically degrades mRNA so that shortened protocols are needed. Here, we present a novel method that allows fluorescence double labeling to be performed in only one incubation of 5 minutes. Fab fragments directly coupled to fluorochromes are linked to primary antibodies before these complexes are applied to sections. We quantified the influences of fixatives, labeling solutions, and incubation time on the mRNA yield and compared our method with previously proposed protocols. While tissue components, ie, vimentin and Ki67 antigen, were sufficiently stained after only 5 minutes of incubation, the new method produced a minute loss of mRNA that did not significantly differ from that of untreated sections. In contrast, incubation times of 15 and 30 minutes reduced the mRNA yield by 99.8 to 99.9%. Furthermore, incubation periods longer than 5 minutes critically affected the ratio between the target and housekeeping genes tested by factors of up to 10.6. In conclusion, the novel method described here reduces mRNA loss and potential ratio shifts to a level that does not significantly differ from that of unlabeled samples.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prostate-specific antigen mRNA and protein levels in laser microdissected cells of human prostate measured by real-time reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and immuno-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.Hum Pathol. 2008 Oct;39(10):1474-82. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2008.02.012. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Hum Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18619642
-
Isolation by size of epithelial tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer: correlation with real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction results and feasibility of molecular analysis by laser microdissection.Hum Pathol. 2006 Jun;37(6):711-8. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2006.01.026. Hum Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16733212
-
Laser microdissection of immunolabeled astrocytes allows quantification of astrocytic gene expression.J Neurosci Methods. 2004 Sep 30;138(1-2):141-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2004.03.022. J Neurosci Methods. 2004. PMID: 15325122
-
Laser microdissection and RNA analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2005;293:167-85. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-853-6:167. Methods Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16028419 Review.
-
Complementary techniques: laser capture microdissection--increasing specificity of gene expression profiling of cancer specimens.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;593:54-65. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-39978-2_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17265716 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of immunohistochemistry on molecular analysis of tissue samples: implications for microdissection technologies.J Histochem Cytochem. 2011 Jun;59(6):591-600. doi: 10.1369/0022155411404704. Epub 2011 Mar 23. J Histochem Cytochem. 2011. PMID: 21430260 Free PMC article.
-
Expression microdissection adapted to commercial laser dissection instruments.Nat Protoc. 2011 Apr;6(4):457-67. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2010.202. Epub 2011 Mar 18. Nat Protoc. 2011. PMID: 21412274 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Isolation from Cell Specific Subpopulations Using Laser-capture Microdissection Combined with Rapid Immunolabeling.J Vis Exp. 2015 Apr 11;(98):52510. doi: 10.3791/52510. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 25939046 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of laser-induced dissection and transport of histologic specimens.Biophys J. 2007 Dec 15;93(12):4481-500. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.102277. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17766336 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 isoforms in the rabbit oculomotor system.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2011 Aug;21(4):228-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2011.06.001. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2011. PMID: 21703892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freeman WM, Walker SJ, Vrana KE. Quantitative RT-PCR: pitfalls and potential. Biotechniques. 1999;26:112–125. - PubMed
-
- Bustin SA. Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol. 2000;25:169–193. - PubMed
-
- Wang T, Brown MJ. mRNA quantification by real time TaqMan polymerase chain reaction: validation and comparison with RNase protection. Anal Biochem. 1999;269:198–201. - PubMed
-
- Fink L, Seeger W, Ermert L, Hanze J, Stahl U, Grimminger F, Kummer W, Bohle RM. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR after laser-assisted cell picking. Nat Med. 1998;4:1329–1333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

