Phylogenomic analysis of the GIY-YIG nuclease superfamily
- PMID: 16646971
- PMCID: PMC1564403
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-98
Phylogenomic analysis of the GIY-YIG nuclease superfamily
Abstract
Background: The GIY-YIG domain was initially identified in homing endonucleases and later in other selfish mobile genetic elements (including restriction enzymes and non-LTR retrotransposons) and in enzymes involved in DNA repair and recombination. However, to date no systematic search for novel members of the GIY-YIG superfamily or comparative analysis of these enzymes has been reported.
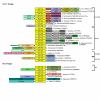
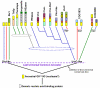
Results: We carried out database searches to identify all members of known GIY-YIG nuclease families. Multiple sequence alignments together with predicted secondary structures of identified families were represented as Hidden Markov Models (HMM) and compared by the HHsearch method to the uncharacterized protein families gathered in the COG, KOG, and PFAM databases. This analysis allowed for extending the GIY-YIG superfamily to include members of COG3680 and a number of proteins not classified in COGs and to predict that these proteins may function as nucleases, potentially involved in DNA recombination and/or repair. Finally, all old and new members of the GIY-YIG superfamily were compared and analyzed to infer the phylogenetic tree.
Conclusion: An evolutionary classification of the GIY-YIG superfamily is presented for the very first time, along with the structural annotation of all (sub)families. It provides a comprehensive picture of sequence-structure-function relationships in this superfamily of nucleases, which will help to design experiments to study the mechanism of action of known members (especially the uncharacterized ones) and will facilitate the prediction of function for the newly discovered ones.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

