The new IL-1 family member IL-1F8 stimulates production of inflammatory mediators by synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes
- PMID: 16646978
- PMCID: PMC1526623
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1946
The new IL-1 family member IL-1F8 stimulates production of inflammatory mediators by synovial fibroblasts and articular chondrocytes
Abstract
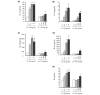
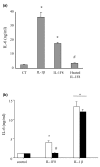
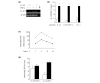
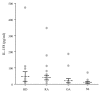
Six novel members of the IL-1 family of cytokines were recently identified, primarily through the use of DNA database searches for IL-1 homologues, and were named IL-1F5 to IL-1F10. In the present study, we investigated the effect of IL-1F8 on primary human joint cells, and examined the expression of the new IL-1 family members in human and mouse joints. Human synovial fibroblasts (hSFs) and human articular chondrocytes (hACs) expressed the IL-1F8 receptor (IL-1Rrp2) and produced pro-inflammatory mediators in response to recombinant IL-1F8. IL-1F8 mRNA expression was increased in hSFs upon stimulation with proinflammatory cytokines, whereas in hACs IL-1F8 mRNA expression was constitutive. However, IL-1F8 protein was undetectable in hSF and hAC culture supernatants. Furthermore, although IL-1beta protein levels were increased in inflamed human and mouse joint tissue, IL-1F8 protein levels were not. IL-1F8 levels in synovial fluids were similar to or lower than those in matched serum samples, suggesting that the joint itself is not a major source of IL-1F8. Serum levels of IL-1F8 were similar in healthy donors, and patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and septic shock, and did not correlate with inflammatory status. Interestingly however, we observed high IL-1F8 levels in several serum samples in all groups. In conclusion, IL-1F8 exerts proinflammatory effects in primary human joint cells. Joint and serum IL-1F8 protein levels did not correlate with inflammation, but they were high in some human serum samples tested, including samples from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. It remains to be determined whether circulating IL-1F8 can contribute to joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Galectin-1 and galectin-3 expression in equine mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), synovial fibroblasts and chondrocytes, and the effect of inflammation on MSC motility.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;8(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0691-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096716 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell activation and its relation to proinflammatory cytokine production in the rheumatoid lesion.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(1):65-74. doi: 10.1186/ar70. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11219391 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding family of interleukin-1 cytokines and their role in destructive inflammatory disorders.Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 Aug;149(2):217-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03441.x. Epub 2007 Jun 21. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17590166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon beta stimulates interleukin 1 receptor antagonist production in human articular chondrocytes and synovial fibroblasts.Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Jan;63(1):43-9. doi: 10.1136/ard.2002.005546. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. PMID: 14672890 Free PMC article.
-
[Immunology of the primary inflamed joint].Z Gesamte Inn Med. 1987 Aug 1;42(15):423-8. Z Gesamte Inn Med. 1987. PMID: 3314204 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Blockade of IL-36 receptor signaling does not prevent from TNF-induced arthritis.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 11;9(8):e101954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101954. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25111378 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Levels of Interleukins 36α, 36β, and 37 in Patients with Psoriasis and Their Correlation with Disease Activity Parameters.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 6;11(18):5254. doi: 10.3390/jcm11185254. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36142901 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of PPARbeta/delta causes a psoriasis-like skin disease in vivo.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 16;5(3):e9701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009701. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20300524 Free PMC article.
-
IL-36 cytokines in autoimmunity and inflammatory disease.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 1;9(2):2895-2901. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22814. eCollection 2018 Jan 5. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29416822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct expression of interleukin (IL)-36α, β and γ, their antagonist IL-36Ra and IL-38 in psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 May;184(2):159-73. doi: 10.1111/cei.12761. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26701127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barton JL, Herbst R, Bosisio D, Higgins L, Nicklin MJ. A tissue specific IL-1 receptor antagonist homolog from the IL-1 cluster lacks IL-1, IL-1ra, IL-18 and IL-18 antagonist activities. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:3299–3308. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200011)30:11<3299::AID-IMMU3299>3.0.CO;2-S. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Debets R, Timans JC, Homey B, Zurawski S, Sana TR, Lo S, Wagner J, Edwards G, Clifford T, Menon S, et al. Two novel IL-1 family members, IL-1 delta and IL-1 epsilon, function as an antagonist and agonist of NF-kappa B activation through the orphan IL-1 receptor-related protein 2. J Immunol. 2001;167:1440–1446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

