Bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis can be repaired through reduction in disease activity with conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
- PMID: 16646983
- PMCID: PMC1526642
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1943
Bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis can be repaired through reduction in disease activity with conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
Abstract
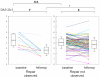
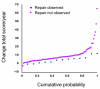
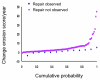
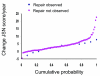
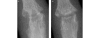
We conducted the present study to determine whether repair of erosions occurs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated with conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and to compare clinical characteristics between patients exhibiting and not exhibiting erosion repair. We included in the study a total of 122 RA patients who fulfilled the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria for RA; all patients had paired sequential radiographs of both hands and wrists showing erosive changes at baseline. Patients were classified into two groups according to the presence of repair of erosions at follow up, namely the 'repair observed' and 'repair not observed' groups. Clinical characteristics, disease activity, radiographic scores and treatment in the two groups were compared. Forty-four repairs were observed in 13 patients (10.7%). Compared with the repair not observed group, the functional class of the patients in the repair observed group was lower at baseline (P < 0.01) and the mean disease activity was lower at follow up (P < 0.005). The changes in radiographic scores per year (total radiographic score and erosion score) were lower (P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively) in the repair observed group. No difference in treatment was observed. Repair of erosions was detected in 10.7% of RA patients treated with conventional DMARDs. Repairs were associated with low functional class at baseline and low disease activity at follow up. These observations support the importance of reduction in disease activity in RA patients. Because repair of erosions was detected in a substantial number of patients, assessment of erosion repair should be incorporated into the radiographic evaluation and scoring of RA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Repair of erosions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with etanercept: magnetic resonance imaging findings after 1 year of follow-up.Scand J Rheumatol. 2013;42(6):437-44. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2013.776104. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Scand J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23607571
-
Assessment of 3-month changes in bone microstructure under anti-TNFα therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT).Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Oct 4;19(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1430-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28978352 Free PMC article.
-
Very recent onset arthritis--clinical, laboratory, and radiological findings during the first year of disease.J Rheumatol. 2002 Nov;29(11):2278-87. J Rheumatol. 2002. PMID: 12415582
-
New Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments for 'Old' Patients: Results of a Systematic Review.Adv Ther. 2020 Sep;37(9):3676-3691. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01435-6. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32705531 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) on bone homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Apr;31(2):689-697. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01088-7. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36348208 Review.
Cited by
-
Multimodal [18 F]FDG PET/CT Is a Direct Readout for Inflammatory Bone Repair: A Longitudinal Study in TNFα Transgenic Mice.J Bone Miner Res. 2019 Sep;34(9):1632-1645. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3748. Epub 2019 Jul 30. J Bone Miner Res. 2019. PMID: 31063606 Free PMC article.
-
Radiographic progression in weight-bearing joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis after TNF-blocking therapies.Clin Rheumatol. 2009 Apr;28(4):453-60. doi: 10.1007/s10067-008-1076-9. Epub 2008 Dec 23. Clin Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19104753
-
Subtle changes in individual joints result in both positive and negative change scores in a patient: results from a clinical trial in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2009 Nov;68(11):1691-5. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.097816. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009. PMID: 19029169 Free PMC article.
-
MRI and ultrasound of the hands and wrists in rheumatoid arthritis. I. Imaging findings.Skeletal Radiol. 2019 May;48(5):677-695. doi: 10.1007/s00256-019-03179-z. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Skeletal Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30796506 Review.
-
PADI4 and HLA-DRB1 are genetic risks for radiographic progression in RA patients, independent of ACPA status: results from the IORRA cohort study.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61045. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061045. Epub 2013 Apr 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brower AC. Use of the radiograph to measure the course of rheumatoid arthritis. The gold standard versus fool's gold. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:316–324. - PubMed
-
- Moeser PJ, Baer AN. Healing of joint erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:151–152. - PubMed
-
- Buckland-Wright JC, Clarke GS, Chikanza IC, Grahame R. Quantitative microfocal radiography detects changes in erosion area in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis treated with myocrisine. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:243–247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

