Atherogenic lipid profile is a feature characteristic of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: effect of early treatment--a prospective, controlled study
- PMID: 16646989
- PMCID: PMC1526648
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1952
Atherogenic lipid profile is a feature characteristic of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: effect of early treatment--a prospective, controlled study
Abstract
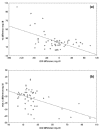
We investigated lipid profiles and lipoprotein modification after immuno-intervention in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (ERA). Fifty-eight patients with ERA who met the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria were included in the study. These patients had disease durations of less than one year and had not had prior treatment for it. Smokers or patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, liver or kidney disease, Cushing's syndrome, obesity, familiar dyslipidemia and those receiving medications affecting lipid metabolism were excluded from the study. Sixty-three healthy volunteers (controls) were also included. Patients were treated with methotrexate and prednisone. Lipid profiles, disease activity for the 28 joint indices score (DAS-28) as well as ACR 50% response criteria were determined for all patients. The mean DAS-28 at disease onset was 5.8 +/- 0.9. After a year of therapy, 53 (91.3%) patients achieved the ACR 20% response criteria, while 45 (77.6%) attained the ACR 50% criteria. In addition, a significant decrease in the DAS-28, C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were observed. ERA patients exhibited higher serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglycerides, whereas their serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were significantly lower compared to controls. As a consequence, the atherogenic ratio of TC/HDL-C as well as that of LDL-C/HDL-C was significantly higher in ERA patients compared to controls. After treatment, a significant reduction of the atherogenic ratio of TC/HDL-C as well as that of LDL-C/HDL-C was observed, a phenomenon primarily due to the increase of serum HDL-C levels. These changes were inversely correlated with laboratory changes, especially CRP and ESR. In conclusion, ERA patients are characterized by an atherogenic lipid profile, which improves after therapy. Thus, early immuno-intervention to control disease activity may reduce the risk of the atherosclerotic process and cardiovascular events in ERA patients.
Figures

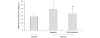
Similar articles
-
Effects of 12 months of treatment with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs on low and high density lipoprotein subclass distribution in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study.Scand J Rheumatol. 2013;42(3):169-75. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2012.745013. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Scand J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23311768
-
Serum Lipid Alterations in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatoid Therapy.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2017 Mar;32(1):26-32. doi: 10.1007/s12291-016-0566-9. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28149009 Free PMC article.
-
Early treatment reduces the cardiovascular risk factors in newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis patients.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Aug;38(1):13-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2007.09.008. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18191989
-
Beyond low-density lipoprotein: addressing the atherogenic lipid triad in type 2 diabetes mellitus and the metabolic syndrome.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005;5(6):379-87. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200505060-00005. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16259526 Review.
-
Pitavastatin: novel effects on lipid parameters.Atheroscler Suppl. 2011 Nov;12(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(11)70887-X. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011. PMID: 22152282 Review.
Cited by
-
The Composition of the HDL Particle and Its Capacity to Remove Cellular Cholesterol Are Associated with a Reduced Risk of Developing Active Inflammatory Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 12;25(20):10980. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010980. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456762 Free PMC article.
-
Use of lipid-lowering agents in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study.J Rheumatol. 2013 Jul;40(7):1082-8. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.121302. Epub 2013 May 1. J Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23637326 Free PMC article.
-
Association between lipid profile and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Med (Lond). 2023 Nov;23(Suppl 6):9-10. doi: 10.7861/clinmed.23-6-s9. Clin Med (Lond). 2023. PMID: 38182228 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A comparative analysis of serological parameters and oxidative stress in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Aug;32(8):2377-82. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-1964-1. Epub 2011 Jun 5. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21644045
-
Prevention of Stroke in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2015 Dec;15(12):77. doi: 10.1007/s11910-015-0600-y. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26486791 Review.
References
-
- Isomaki HA, Mutru O, Koota K. Death rate and causes of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1975;4:205–208. - PubMed
-
- Watson DJ, Rhodes T, Guess HA. All-cause mortality and vascular events among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, or no arthritis in the UK General Practice Research Database. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:1196–1202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

