Defining the global spatial limits of malaria transmission in 2005
- PMID: 16647970
- PMCID: PMC3145102
- DOI: 10.1016/S0065-308X(05)62005-2
Defining the global spatial limits of malaria transmission in 2005
Abstract
There is no accurate contemporary global map of the distribution of malaria. We show how guidelines formulated to advise travellers on appropriate chemoprophylaxis for areas of reported Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax malaria risk can be used to generate crude spatial limits. We first review and amalgamate information on these guidelines to define malaria risk at national and sub-national administrative boundary levels globally. We then adopt an iterative approach to reduce these extents by applying a series of biological limits imposed by altitude, climate and population density to malaria transmission, specific to the local dominant vector species. Global areas of, and population at risk from, P. falciparum and often-neglected P. vivax malaria are presented for 2005 for all malaria endemic countries. These results reveal that more than 3 billion people were at risk of malaria in 2005.
Figures
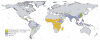
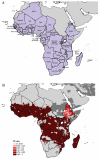















References
-
- Bates I, Fenton C, Gruber J, Lalloo D, Lara A. Medina, Squire SB, Theobald S, Thomson R, Tolhurst R. Vulnerability to malaria, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS infection and disease. Part 1: determinants operating at individual and household level. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2004;4:267–277. - PubMed
-
- Beljaev AE. Determinants of malaria in the Middle East and North Africa. In: Casman EA, Dowlatabadi H, editors. The Contextual Determinants of Malaria. Resources for the Future Press; Washington, DC: 2002. pp. 137–166.
-
- Boyd MF. Malariology. W.B. Saunders; Philadelphia: 1949.
-
- CDC . Health information for international travel 2003– 2004. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta: 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

