Microfabricated bioprocessor for integrated nanoliter-scale Sanger DNA sequencing
- PMID: 16648246
- PMCID: PMC1464327
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0602476103
Microfabricated bioprocessor for integrated nanoliter-scale Sanger DNA sequencing
Abstract
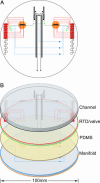
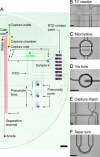
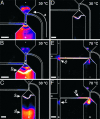
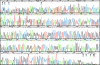
An efficient, nanoliter-scale microfabricated bioprocessor integrating all three Sanger sequencing steps, thermal cycling, sample purification, and capillary electrophoresis, has been developed and evaluated. Hybrid glass-polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) wafer-scale construction is used to combine 250-nl reactors, affinity-capture purification chambers, high-performance capillary electrophoresis channels, and pneumatic valves and pumps onto a single microfabricated device. Lab-on-a-chip-level integration enables complete Sanger sequencing from only 1 fmol of DNA template. Up to 556 continuous bases were sequenced with 99% accuracy, demonstrating read lengths required for de novo sequencing of human and other complex genomes. The performance of this miniaturized DNA sequencer provides a benchmark for predicting the ultimate cost and efficiency limits of Sanger sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: R.A.M. is a consultant with Microchip Biotechnologies Inc. (MBI) and has a financial interest in MBI. MBI is working on the commercialization of microchip sequencing technologies and may benefit from the results of this research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microchip bioprocessor for integrated nanovolume sample purification and DNA sequencing.Anal Chem. 2002 Oct 1;74(19):5092-8. doi: 10.1021/ac0203645. Anal Chem. 2002. PMID: 12380835
-
Inline injection microdevice for attomole-scale sanger DNA sequencing.Anal Chem. 2007 Jun 15;79(12):4499-506. doi: 10.1021/ac070126f. Epub 2007 May 12. Anal Chem. 2007. PMID: 17497827
-
Eight hundred-base sequencing in a microfabricated electrophoretic device.Anal Chem. 2000 Jul 15;72(14):3388-91. doi: 10.1021/ac9913614. Anal Chem. 2000. PMID: 10939418
-
Microfluidic devices for DNA sequencing: sample preparation and electrophoretic analysis.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2003 Feb;14(1):42-50. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(02)00004-6. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12566001 Review.
-
Nanopore sequencing technology: research trends and applications.Trends Biotechnol. 2006 Dec;24(12):580-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.10.005. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Trends Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17055093 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated microdevice of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction with colorimetric immunochromatographic detection for rapid gene expression analysis of influenza A H1N1 virus.Biosens Bioelectron. 2012 Mar 15;33(1):88-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.12.024. Epub 2012 Jan 8. Biosens Bioelectron. 2012. PMID: 22265877 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling transcriptome based on transcript-sampling data.PLoS One. 2008 Feb 20;3(2):e1659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001659. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18286206 Free PMC article.
-
Leakage pressures for gasketless superhydrophobic fluid interconnects for modular lab-on-a-chip systems.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2021 Sep 2;7:69. doi: 10.1038/s41378-021-00287-6. eCollection 2021. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2021. PMID: 34567781 Free PMC article.
-
DNA sequencing: bench to bedside and beyond.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(18):6227-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm688. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17855400 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophoretic separations on microfluidic chips.J Chromatogr A. 2008 Mar 14;1184(1-2):542-59. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.119. Epub 2007 Dec 23. J Chromatogr A. 2008. PMID: 18207148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheng Z., Ventura M., She X. W., Khaitovich P., Graves T., Osoegawa K., Church D., DeJong P., Wilson R. K., Paabo S., et al. Nature. 2005;437:88–93. - PubMed
-
- Check E. Nature. 2005;437:1084–1086. - PubMed
-
- National Institutes of Health. Near-Term Technology Development for Genome Sequencing. Bethesda: Natl. Inst. of Health; 2004. Feb 12, RFA-HG-04-002.
-
- Shendure J., Porreca G. J., Reppas N. B., Lin X. X., McCutcheon J. P., Rosenbaum A. M., Wang M. D., Zhang K., Mitra R. D., Church G. M. Science. 2005;309:1728–1732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

