Deoxyribozymes that recode sequence information
- PMID: 16648360
- PMCID: PMC1450334
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl176
Deoxyribozymes that recode sequence information
Abstract
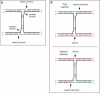
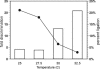
Allosteric nucleic acid ligases have been used previously to transform analyte-binding into the formation of oligonucleotide templates that can be amplified and detected. We have engineered binary deoxyribozyme ligases whose two components are brought together by bridging oligonucleotide effectors. The engineered ligases can 'read' one sequence and then 'write' (by ligation) a separate, distinct sequence, which can in turn be uniquely amplified. The binary deoxyribozymes show great specificity, can discriminate against a small number of mutations in the effector, and can read and recode DNA information with high fidelity even in the presence of excess obscuring genomic DNA. In addition, the binary deoxyribozymes can read non-natural nucleotides and write natural sequence information. The binary deoxyribozyme ligases could potentially be used in a variety of applications, including the detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms in genomic DNA or the identification of short nucleic acids such as microRNAs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deoxyribozyme-based ligase logic gates and their initial circuits.J Am Chem Soc. 2005 May 18;127(19):6914-5. doi: 10.1021/ja043003a. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. PMID: 15884910
-
ATP-dependent allosteric DNA enzymes.Chem Biol. 2002 Apr;9(4):417-26. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(02)00123-0. Chem Biol. 2002. PMID: 11983331
-
Using a deoxyribozyme ligase and rolling circle amplification to detect a non-nucleic acid analyte, ATP.J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Feb 23;127(7):2022-3. doi: 10.1021/ja043490u. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. PMID: 15713061
-
Deoxyribozymes: useful DNA catalysts in vitro and in vivo.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Jul;65(14):2156-74. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8029-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18373062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catalytic DNA (deoxyribozymes) for synthetic applications-current abilities and future prospects.Chem Commun (Camb). 2008 Aug 14;(30):3467-85. doi: 10.1039/b807292m. Epub 2008 Jul 1. Chem Commun (Camb). 2008. PMID: 18654692 Review.
Cited by
-
A binary deoxyribozyme for nucleic acid analysis.Chembiochem. 2007 Nov 23;8(17):2039-42. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200700384. Chembiochem. 2007. PMID: 17924377 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mismatch Discrimination and Efficient Photomodulation with Split 10-23 DNAzymes.Inorganica Chim Acta. 2012 Jan 15;380:386-391. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2011.10.068. Inorganica Chim Acta. 2012. PMID: 22544974 Free PMC article.
-
DNA as a versatile chemical component for catalysis, encoding, and stereocontrol.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010 Sep 24;49(40):7180-201. doi: 10.1002/anie.200906345. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010. PMID: 20669202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shaping up nucleic acid computation.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2010 Aug;21(4):392-400. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20538451 Free PMC article.
-
A simple DNA-based translation system.Nano Lett. 2007 Feb;7(2):480-3. doi: 10.1021/nl0628605. Epub 2007 Jan 23. Nano Lett. 2007. PMID: 17243754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Battiste J.L., Mao H., Rao N.S., Tan R., Muhandiram D.R., Kay L.E., Frankel A.D., Williamson J.R. Alpha helix-RNA major groove recognition in an HIV-1 rev peptide–RRE RNA complex. Science. 1996;273:1547–1551. - PubMed
-
- Legault P., Li J., Mogridge J., Kay L.E., Greenblatt J. NMR structure of the bacteriophage lambda N peptide/boxB RNA complex: recognition of a GNRA fold by an arginine-rich motif. Cell. 1998;93:289–299. - PubMed
-
- Levy M., Ellington A.D. ATP-dependent allosteric DNA enzymes. Chem. Biol. 2002;9:417–426. - PubMed
-
- Koizumi M., Soukup G.A., Kerr J.N., Breaker R.R. Allosteric selection of ribozymes that respond to the second messengers cGMP and cAMP. Nature Struct. Biol. 1999;6:1062–1071. - PubMed

