Tethering KSRP, a decay-promoting AU-rich element-binding protein, to mRNAs elicits mRNA decay
- PMID: 16648466
- PMCID: PMC1489004
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.10.3695-3706.2006
Tethering KSRP, a decay-promoting AU-rich element-binding protein, to mRNAs elicits mRNA decay
Abstract
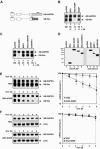
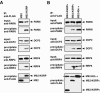
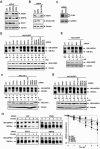
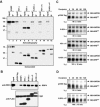
Inherently unstable mRNAs contain AU-rich elements (AREs) in their 3' untranslated regions that act as mRNA stability determinants by interacting with ARE-binding proteins (ARE-BPs). We have destabilized two mRNAs by fusing sequence-specific RNA-binding proteins to KSRP, a decay-promoting ARE-BP, in a tethering assay. These results support a model that KSRP recruits mRNA decay machinery/factors to elicit decay. The ability of tethered KSRP to elicit mRNA decay depends on functions of known mRNA decay enzymes. By targeting the Rev response element of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by using Rev-KSRP fusion protein, we degraded viral mRNA, resulting in a dramatic reduction of viral replication. These results provide a foundation for the development of novel therapeutic strategies to inhibit specific gene expression in patients with acquired or hereditary diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Bevilacqua, A., M. C. Ceriani, S. Capaccioli, and A. Nicolin. 2003. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression by degradation of messenger RNAs. J. Cell. Physiol. 195:356-372. - PubMed
-
- Blackshear, P. J. 2002. Tristetraprolin and other CCCH tandem zinc-finger proteins in the regulation of mRNA turnover. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 30:945-952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
