Metabolic disruption in Drosophila bang-sensitive seizure mutants
- PMID: 16648587
- PMCID: PMC1526683
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.057463
Metabolic disruption in Drosophila bang-sensitive seizure mutants
Abstract
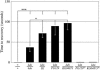
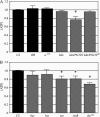
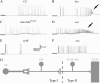
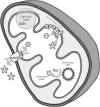
We examined a number of Drosophila mutants with increased susceptibility to seizures following mechanical or electrical stimulation to better understand the underlying factors that predispose neurons to aberrant activity. Several mutations in this class have been molecularly identified and suggest metabolic disruption as a possible source for increased seizure susceptibility. We mapped the bang-sensitive seizure mutation knockdown (kdn) to cytological position 5F3 and identified citrate synthase as the affected gene. These results further support a role for mitochondrial metabolism in controlling neuronal activity and seizure susceptibility. Biochemical analysis in bang-sensitive mutants revealed reductions in ATP levels consistent with disruption of mitochondrial energy production in these mutants. Electrophysiological analysis of mutants affecting mitochondrial proteins revealed an increased likelihood for a specific pattern of seizure activity. Our data implicate cellular metabolism in regulating seizure susceptibility and suggest that differential sensitivity of neuronal subtypes to metabolic changes underlies distinct types of seizure activity.
Figures


References
-
- Attwell, D., and S. B. Laughlin, 2001. An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 21: 1133–1145. - PubMed
-
- Beal, M. F., B. T. Hyman and W. Koroshetz, 1993. Do defects in mitochondrial energy metabolism underlie the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases? Trends Neurosci. 16: 125–131. - PubMed
-
- Benzer, S., 1971. From the gene to behavior. JAMA 218: 1015–1022. - PubMed
-
- Bourbon, H. M., G. Gonzy-Treboul, F. Peronnet, M. F. Alin, C. Ardourel et al., 2002. A P-insertion screen identifying novel X-linked essential genes in Drosophila. Mech. Dev. 110: 71–83. - PubMed
-
- De Meirleir, L., 2002. Defects of pyruvate metabolism and the Krebs cycle. J. Child Neurol. 17(Suppl. 3): 3S26–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

