The development of aggression in 18 to 48 month old children of alcoholic parents
- PMID: 16649002
- PMCID: PMC2666196
- DOI: 10.1007/s10802-006-9021-3
The development of aggression in 18 to 48 month old children of alcoholic parents
Abstract
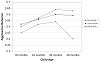
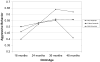
This study examined the development of aggressive and oppositional behavior among alcoholic and nonalcoholic families using latent growth modeling. The sample consisted of 226 families assessed at 18, 24, 36, and 48 months of child age. Results indicated that children in families with nonalcoholic parents had the lowest levels of aggressive behavior at all time points compared to children with one or more alcoholic parents. Children in families with two alcoholic parents did not exhibit normative decreases in aggressive behavior from 3 to 4 years of age compared to nonalcoholic families. However, this association was no longer significant once a cumulative family risk score was added to the model. Children in families with high cumulative risk scores, reflective of high parental depression, antisocial behavior, negative affect during play, difficult child temperament, marital conflict, fathers' education, and hours spent in child care, had higher levels of aggression at 18 months than children in low risk families. These associations were moderated by child gender. Boys had higher levels of aggressive behavior at all ages than girls, regardless of group status. Cumulative risk was predictive of higher levels of initial aggressive behavior in both girls and boys. However, boys with two alcoholic parents had significantly less of a decline in aggression from 36 to 48 months compared to boys in the nonalcoholic group.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of effortful control among children of alcoholic and nonalcoholic fathers.J Stud Alcohol. 2004 May;65(3):309-19. doi: 10.15288/jsa.2004.65.309. J Stud Alcohol. 2004. PMID: 15222587
-
A conceptual model predicting internalizing problems in middle childhood among children of alcoholic and nonalcoholic fathers: the role of marital aggression.J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2009 Sep;70(5):741-50. doi: 10.15288/jsad.2009.70.741. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19737499 Free PMC article.
-
Parent-infant interactions among families with alcoholic fathers.Dev Psychopathol. 1999 Fall;11(4):745-62. doi: 10.1017/s0954579499002308. Dev Psychopathol. 1999. PMID: 10624724 Free PMC article.
-
Attachment relationships among children with aggressive behavior problems: the role of disorganized early attachment patterns.J Consult Clin Psychol. 1996 Feb;64(1):64-73. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.64.1.64. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1996. PMID: 8907085 Review.
-
[Homosexual parenthood and child development: present data].Encephale. 2012 Feb;38(1):10-5. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.05.005. Epub 2011 Jul 5. Encephale. 2012. PMID: 22381718 Review. French.
Cited by
-
A conceptual model for the development of externalizing behavior problems among kindergarten children of alcoholic families: role of parenting and children's self-regulation.Dev Psychol. 2007 Sep;43(5):1187-201. doi: 10.1037/0012-1649.43.5.1187. Dev Psychol. 2007. PMID: 17723044 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal cocaine use and mother-toddler aggression.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2011 May-Jun;33(3):360-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2011. PMID: 21396441 Free PMC article.
-
The relation of parent alcohol disorder to young adult drinking outcomes mediated by parenting: Effects of developmentally limited versus persistent parent alcohol disorder.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018 Jul 1;188:224-231. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2018.03.027. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018. PMID: 29783094 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental cascade model for adolescent substance use from infancy to late adolescence.Dev Psychol. 2016 Oct;52(10):1619-1633. doi: 10.1037/dev0000199. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Dev Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27584669 Free PMC article.
-
Dimensional Latent Structure of Early Disruptive Behavior Disorders: A Taxometric Analysis in Preschoolers.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2018 Oct;46(7):1385-1394. doi: 10.1007/s10802-017-0383-5. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29243197
References
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the child behavior checklist/2–3 and 1992 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry; 1992.
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Manual for ASEBA preschool forms and profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families; 2000.
-
- Achenbach TM, Edelbrock C, Howell C. Empirically based assessment of the behavioral/emotional problems of 2- and 3-year-old children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 1987;15:629–650. - PubMed
-
- Andreason NC, Rice J, Endicott J, Reich T, Coryell W. The family history approach to diagnosis. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1986;43:421–429. - PubMed
-
- Anthony JC, Warner LA, Kessler RC. Comparative epidemiology of dependence on tobacco, alcohol, controlled substances, and inhalants: Basic findings from the National Comorbidity Survey. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 1994;2:244–268.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical