A functional network involved in the recycling of nucleocytoplasmic pre-60S factors
- PMID: 16651379
- PMCID: PMC2063836
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200510080
A functional network involved in the recycling of nucleocytoplasmic pre-60S factors
Abstract
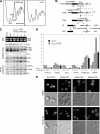
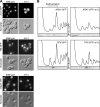
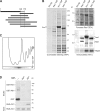
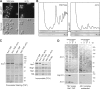
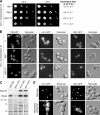
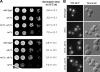
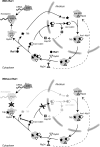
Eukaryotic pre-ribosomes go through cytoplasmic maturation steps before entering translation. The nucleocytoplasmic proteins participating in these late stages of maturation are reimported to the nucleus. In this study, we describe a functional network focused on Rei1/Ybr267w, a strictly cytoplasmic pre-60S factor indirectly involved in nuclear 27S pre-ribosomal RNA processing. In the absence of Rei1, the nuclear import of at least three other pre-60S factors is impaired. The accumulation in the cytoplasm of a small complex formed by the association of Arx1 with a novel factor, Alb1/Yjl122w, inhibits the release of the putative antiassociation factor Tif6 from the premature large ribosomal subunits and its recycling to the nucleus. We propose a model in which Rei1 is a key factor for the coordinated dissociation and recycling of the last pre-60S factors before newly synthesized large ribosomal subunits enter translation.
Figures

References
-
- Bassler, J., P. Grandi, O. Gadal, T. Lessmann, E. Petfalski, D. Tollervey, J. Lechner, and E. Hurt. 2001. Identification of a 60S preribosomal particle that is closely linked to nuclear export. Mol. Cell. 8:517–529. - PubMed
-
- Brachmann, C.B., A. Davies, G.J. Cost, E. Caputo, J. Li, P. Hieter, and J.D. Boeke. 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast. 14:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Dez, C., and D. Tollervey. 2004. Ribosome synthesis meets the cell cycle. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 7:631–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

