Tracking germinal center B cells expressing germ-line immunoglobulin gamma1 transcripts by conditional gene targeting
- PMID: 16651521
- PMCID: PMC1464351
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0602353103
Tracking germinal center B cells expressing germ-line immunoglobulin gamma1 transcripts by conditional gene targeting
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 6;104(6):2025. Segal, Jane [corrected to Seagal, Jane]
Abstract
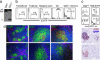
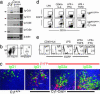
Germinal centers (GCs) represent the main sites for the generation of high-affinity, class-switched antibodies during T cell-dependent antibody responses. To study gene function specifically in GC B cells, we generated Cgamma1-cre mice in which the expression of Cre recombinase is induced by transcription of the Ig gamma1 constant region gene segment (Cgamma1). In these mice, Cre-mediated recombination at the fas, Igbeta, IgH, and Rosa26 loci occurred in GC B cells as early as 4 days after immunization with T cell-dependent antigens and involved >85% of GC B cells at the peak of the GC reaction. Less than 2% of IgM(+) B cells showed Cre-mediated recombination. These cells carried few Ig somatic mutations, expressed germ-line Cgamma1- and activation-induced cytidine deaminase-specific transcripts and likely include GC B cell founders and/or plasma cell precursors. Cre-mediated recombination involved most IgG1, but also a fraction of IgG3-, IgG2a-, IgG2b-, and IgA-expressing GC and post-GC B cells. This result indicates that a GC B cell can transcribe more than one downstream C(H) gene before undergoing class switch recombination. The efficient induction of Cre expression in GC B cells makes the Cgamma1-cre allele a powerful tool for the genetic analysis of these cells, as well as, in combination with a suitable marker for Cre-mediated recombination, the tracking of class-switched memory B and plasma cells in vivo. To expedite the genetic analysis of GC B cells, we have established Cgamma1-cre F(1) embryonic stem cells, allowing further rounds of gene targeting and the cloning of compound mutants by tetraploid embryo complementation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures



References
-
- MacLennan I. C. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994;12:117–139. - PubMed
-
- Garside P., Ingulli E., Merica R. R., Johnson J. G., Noelle R. J., Jenkins M. K. Science. 1998;281:96–99. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y. J., Zhang J., Lane P. J., Chan E. Y., MacLennan I. C. Eur. J. Immunol. 1991;21:2951–2962. - PubMed
-
- Allen C. D., Ansel K. M., Low C., Lesley R., Tamamura H., Fujii N., Cyster J. G. Nat. Immunol. 2004;5:943–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

