Hepatocyte growth factor attenuates liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation
- PMID: 16651617
- PMCID: PMC1606599
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050747
Hepatocyte growth factor attenuates liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation
Abstract
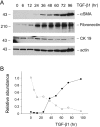
Hepatic fibrosis is a common outcome of a variety of chronic liver diseases. Here we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) on liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation (BDL) and investigated potential mechanisms. Mice underwent BDL, followed by intravenous injections of naked HGF expression plasmid or control vector. HGF gene therapy markedly ameliorated hepatic fibrotic lesions, as demonstrated by reduced alpha-smooth muscle actin (alphaSMA) expression, attenuated deposition of type I and type III collagen, and normalized total hydroxyproline content. HGF also suppressed transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) expression. Interestingly, colocalization of alphaSMA and cytokeratin-19 in bile duct epithelium was observed, suggesting the possibility of biliary epithelial to myofibroblast transition after BDL. Cells that were still positive for cytokeratin-19 but actively producing type I collagen were found in the biliary epithelia and periductal region. Laminin staining revealed an impaired basement membrane of the bile duct epithelium in diseased liver. These lesions were largely prevented by HGF administration. In vitro, treatment of human biliary epithelial cells with TGF-beta1 induced alphaSMA and fibronectin expression and suppressed cytokeratin-19. HGF abolished the phenotypic conversion of biliary epithelial cells induced by TGF-beta1. These results suggest that HGF ameliorates hepatic biliary fibrosis in part by blocking bile duct epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
Figures

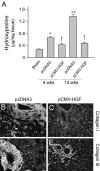

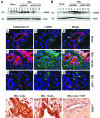

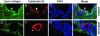
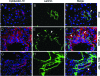

References
-
- Pinzani M, Rombouts K. Liver fibrosis: from the bench to clinical targets. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36:231–242. - PubMed
-
- Albanis E, Friedman SL. Hepatic fibrosis. Pathogenesis and principles of therapy. Clin Liver Dis. 2001;5:315–334, v–vi. - PubMed
-
- Eng FJ, Friedman SL. Fibrogenesis I. New insights into hepatic stellate cell activation: the simple becomes complex. Am J Physiol. 2000;279:G7–G11. - PubMed
-
- Lunz JG, III, Contrucci S, Ruppert K, Murase N, Fung JJ, Starzl TE, Demetris AJ. Replicative senescence of biliary epithelial cells precedes bile duct loss in chronic liver allograft rejection: increased expression of p21(WAF1/Cip1) as a disease marker and the influence of immunosuppressive drugs. Am J Pathol. 2001;158:1379–1390. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

