Gangliosides trigger inflammatory responses via TLR4 in brain glia
- PMID: 16651628
- PMCID: PMC1606595
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050924
Gangliosides trigger inflammatory responses via TLR4 in brain glia
Abstract
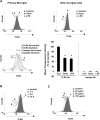
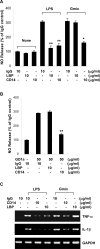
Gangliosides participate in various cellular events of the central nervous system and have been closely implicated in many neuronal diseases. However, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying the pathological activity of gangliosides are poorly understood. Here we report that toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) may mediate the ganglioside-triggered inflammation in glia, brain resident immune cells. Gangliosides rapidly altered the cell surface expression of TLR4 in microglia and astrocytes within 3 hours. Using TLR4-specific siRNA and a dominant-negative TLR4 gene, we clearly demonstrate the functional importance of TLR4 in ganglioside-triggered activation of glia. Inhibition of TLR4 expression by TLR4-siRNA suppressed nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-binding activity, NF-kappaB-dependent luciferase activity, and transcription of inflammatory cytokines after exposure to gangliosides. Transient transfection of dominant-negative TLR4 also attenuated NF-kappaB-binding activity and interleukin-6 promoter activity. In contrast, these activities were slightly elevated in cells with wild-type TLR4. In addition, CD14 was required for ganglioside-triggered activation of glia, and lipid raft formation may be associated with ganglioside-stimulated signal propagation. Taken together, these results suggest that TLR4 may provide an explanation for the pathological ability of gangliosides to cause inflammatory conditions in the brain.
Figures


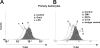

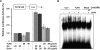


Similar articles
-
Contribution of TLR2 to the initiation of ganglioside-triggered inflammatory signaling.Mol Cells. 2008 Feb 29;25(1):99-104. Mol Cells. 2008. PMID: 18319620
-
C-reactive protein triggers inflammatory responses partly via TLR4/IRF3/NF-κB signaling pathway in rat vascular smooth muscle cells.Life Sci. 2010 Sep 11;87(11-12):367-74. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.07.012. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20670634
-
Ganglioside GD1a suppresses LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines in RAW264.7 macrophages by reducing MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways through TLR4.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Sep;28(1):136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.05.044. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26054879
-
Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Jul 18;16(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1538-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31319868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Homeostatic and Pathophysiological Regulation of Toll-like Receptor 4 Signaling by GM3 Ganglioside Molecular Species].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022;142(3):195-203. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.21-00193. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 35228371 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Increased Alveolar Heparan Sulphate and Reduced Pulmonary Surfactant Amount and Function in the Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA Mouse.Cells. 2021 Apr 8;10(4):849. doi: 10.3390/cells10040849. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33918094 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory mediators of opioid tolerance: Implications for dependency and addiction.Peptides. 2019 May;115:51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2019.01.003. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Peptides. 2019. PMID: 30890355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ganglioside Synthesis by Plasma Membrane-Associated Sialyltransferase in Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 5;21(3):1063. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031063. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32033474 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of TLR4 reduces neurovascular unit and secondary inflammatory process after traumatic brain injury in mice.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057208. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555560 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) extends survival in the hSOD1 G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 May 13;12:90. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0310-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 25962427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ridet JL, Malhotra SK, Privat A, Gage FH. Reactive astrocytes: cellular and molecular cues to biological function. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:570–577. - PubMed
-
- Matyszak MK. Inflammation in the CNS: balance between immunological privilege and immune responses. Prog Neurobiol. 1998;56:19–35. - PubMed
-
- Streit WJ, Walter SA, Pennell NA. Reactive microgliosis. Prog Neurobiol. 1999;57:563–581. - PubMed
-
- Aloisi F, Ria F, Adorini L. Regulation of T-cell responses by CNS antigen-presenting cells: different roles for microglia and astrocytes. Immunol Today. 2000;21:141–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

