Phytochrome structure and signaling mechanisms
- PMID: 16669784
- PMCID: PMC2664748
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144208
Phytochrome structure and signaling mechanisms
Abstract
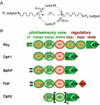
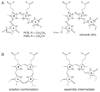
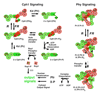
Phytochromes are a widespread family of red/far-red responsive photoreceptors first discovered in plants, where they constitute one of the three main classes of photomorphogenesis regulators. All phytochromes utilize covalently attached bilin chromophores that enable photoconversion between red-absorbing (P(r)) and far-red-absorbing (P(fr)) forms. Phytochromes are thus photoswitchable photosensors; canonical phytochromes have a conserved N-terminal photosensory core and a C-terminal regulatory region, which typically includes a histidine-kinase-related domain. The discovery of new bacterial and cyanobacterial members of the phytochrome family within the last decade has greatly aided biochemical and structural characterization of this family, with the first crystal structure of a bacteriophytochrome photosensory core appearing in 2005. This structure and other recent biochemical studies have provided exciting new insights into the structure of phytochrome, the photoconversion process that is central to light sensing, and the mechanism of signal transfer by this important family of photoreceptors.
Figures


References
-
- Andel F, Lagarias JC, Mathies RA. Resonance Raman analysis of chromophore structure in the lumi-R photoproduct of phytochrome. Biochem. 1996;35:15997–16008. - PubMed
-
- Andel F, Murphy JT, Haas JA, McDowell MT, van der Hoef I, et al. Probing the photoreaction mechanism of phytochrome through analysis of resonance Raman vibrational spectra of recombinant analogues. Biochem. 2000;39:2667–2676. - PubMed
-
- Batschauer A, editor. Photoreceptors and Light Signaling. Vols. 3. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry; 2003. 388 pp.
-
- Bhoo SH, Davis SJ, Walker J, Karniol B, Vierstra RD. Bacteriophytochromes are photochromic histidine kinases using a biliverdin chromophore. Nature. 2001;414:776–779. - PubMed
-
- Blumenstein A, Vienken K, Tasler R, Purschwitz J, Veith D, et al. The Aspergillus nidulans phytochrome FphA represses sexual development in red light. Curr. Biol. 2005;15:1833–1838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

