Prevalence of HIV infection among young adults in the United States: results from the Add Health study
- PMID: 16670236
- PMCID: PMC1470623
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2004.054759
Prevalence of HIV infection among young adults in the United States: results from the Add Health study
Abstract
Objectives: We estimated HIV prevalence rates among young adults in the United States.
Methods: We used survey data from the third wave of the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health, a random sample of nearly 19000 young adults initiated in 1994-1995. Consenting respondents were screened for the presence of antibodies to HIV-1 in oral mucosal transudate specimens. We calculated prevalence rates, accounting for survey design, response rates, and test performance.
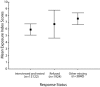
Results: Among the 13184 participants, the HIV prevalence rate was 1.0 per 1000 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.4, 1.7). Gender-specific prevalence rates were similar, but rates differed markedly between non-Hispanic Blacks (4.9 per 1000; 95% CI=1.8, 8.7) and members of other racial/ethnic groups (0.22 per 1000; 95% CI=0.00, 0.64).
Conclusions: Racial disparities in HIV in the United States are established early in the life span, and our data suggest that 15% to 30% of all cases of HIV occur among individuals younger than 25 years.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report, 2003. Washington, DC: US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2004.
-
- Rosenberg PS, Biggar RJ, Goedert JJ. Declining age at HIV infection in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:789–790. - PubMed
-
- Rogers AS. HIV research in American youth. J Adolesc Health. 2001;29(suppl 3):1–4. - PubMed
-
- HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report: US. HIV and AIDS Cases Reported Through December 2001. Atlanta, Ga: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

