HDL from CETP-deficient subjects shows enhanced ability to promote cholesterol efflux from macrophages in an apoE- and ABCG1-dependent pathway
- PMID: 16670775
- PMCID: PMC1451209
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI27602
HDL from CETP-deficient subjects shows enhanced ability to promote cholesterol efflux from macrophages in an apoE- and ABCG1-dependent pathway
Abstract
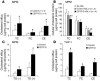
Genetic deficiency or inhibition of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) leads to a marked increase in plasma levels of large HDL-2 particles. However, there is concern that such particles may be dysfunctional in terms of their ability to promote cholesterol efflux from macrophages. Recently, the ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG1, a macrophage liver X receptor (LXR) target, has been shown to stimulate cholesterol efflux to HDL. We have assessed the ability of HDL from subjects with homozygous deficiency of CETP (CETP-D) to promote cholesterol efflux from macrophages and have evaluated the role of ABCG1 and other factors in this process. CETP-D HDL-2 caused a 2- to 3-fold stimulation of net cholesterol efflux compared with control HDL-2 in LXR-activated macrophages, due primarily to an increase in lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase-mediated (LCAT-mediated) cholesteryl ester formation in media. Genetic knockdown or overexpression of ABCG1 showed that increased cholesterol efflux to CETP-D HDL was ABCG1 dependent. LCAT and apoE contents of CETP-D HDL-2 were markedly increased compared with control HDL-2, and increased cholesterol esterification activity resided within the apoE-HDL fraction. Thus, CETP-D HDL has enhanced ability to promote cholesterol efflux from foam cells in an ABCG1-dependent pathway due to an increased content of LCAT and apoE.
Figures
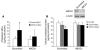
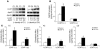
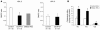
Comment in
-
Putting cholesterol in its place: apoE and reverse cholesterol transport.J Clin Invest. 2006 May;116(5):1226-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI28632. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16670767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glomset J.A. The plasma lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J. Lipid Res. 1968;9:155–167. - PubMed
-
- Ji Y., et al. Scavenger receptor BI promotes high density lipoprotein-mediated cellular cholesterol efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:20982–20985. - PubMed
-
- Wang N., Silver D.L., Thiele C., Tall A.R. ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) functions as a cholesterol efflux regulatory protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:23742–23747. - PubMed
-
- Hara H., Yokoyama S. Role of apolipoproteins in cholesterol efflux from macrophages to lipid microemulsion: proposal of a putative model for pre-beta high density lipoprotein pathway. . Biochemistry. 1992;31:2040–2046. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

