Direct and heterologous approaches to identify the LET-756/FGF interactome
- PMID: 16672054
- PMCID: PMC1513213
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-105
Direct and heterologous approaches to identify the LET-756/FGF interactome
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are multifunctional proteins that play important roles in cell communication, proliferation and differentiation. However, many aspects of their activities are not well defined. LET-756, one of the two C. elegans FGFs, is expressed throughout development and is essential for worm development. It is both expressed in the nucleus and secreted.
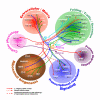
Results: To identify nuclear factors associated with LET-756, we used three approaches. First, we screened a two-hybrid cDNA library derived from mixed stages worms and from a normalized library, using LET-756 as bait. This direct approach allowed the identification of several binding partners that play various roles in the nucleus/nucleolus, such as PAL-1, a transcription regulator, or RPS-16, a component of the small ribosomal subunit. The interactions were validated by co-immunoprecipitation and determination of their site of occurrence in mammalian cells. Second, because patterns of protein interactions may be conserved throughout species, we searched for orthologs of known mammalian interactors and measured binary interaction with these predicted candidates. We found KIN-3 and KIN-10, the orthologs of CK2alpha and CK2beta, as new partners of LET-756. Third, following the assumption that recognition motifs mediating protein interaction may be conserved between species, we screened a two-hybrid cDNA human library using LET-756 as bait. Among the few FGF partners detected was 14-3-3beta. In support of this interaction we showed that the two 14-3-3beta orthologous proteins, FTT-1 and FTT-2/PAR-5, interacted with LET-756.
Conclusion: We have conducted the first extensive search for LET-756 interactors using a multi-directional approach and established the first interaction map of LET-756/FGF with other FGF binding proteins from other species. The interactors identified play various roles in developmental process or basic biochemical events such as ribosome biogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intracellular trafficking of LET-756, a fibroblast growth factor of C. elegans, is controlled by a balance of export and nuclear signals.Exp Cell Res. 2006 May 15;312(9):1484-95. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.01.012. Epub 2006 Feb 20. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16487967
-
Functional phylogeny relates LET-756 to fibroblast growth factor 9.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 17;279(38):40146-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405795200. Epub 2004 Jun 15. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15199049
-
The Doubletime Homolog KIN-20 Mainly Regulates let-7 Independently of Its Effects on the Period Homolog LIN-42 in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Jul 31;8(8):2617-2629. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200392. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29880558 Free PMC article.
-
A pair as a minimum: the two fibroblast growth factors of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.Dev Dyn. 2005 Feb;232(2):247-55. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20219. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 15614779 Review.
-
The barber's pole worm CAP protein superfamily--A basis for fundamental discovery and biotechnology advances.Biotechnol Adv. 2015 Dec;33(8):1744-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Biotechnol Adv. 2015. PMID: 26239368 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods to Study Mrp4-containing Macromolecular Complexes in the Regulation of Fibroblast Migration.J Vis Exp. 2016 May 19;(111):53973. doi: 10.3791/53973. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27285126 Free PMC article.
-
PAR-5 is a PARty hub in the germline: Multitask proteins in development and disease.Worm. 2013 Jan 1;2(1):e21834. doi: 10.4161/worm.21834. Worm. 2013. PMID: 24058859 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-organ signalling by HRG-7 promotes systemic haem homeostasis.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Jul;19(7):799-807. doi: 10.1038/ncb3539. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28581477 Free PMC article.
-
The 14-3-3 protein PAR-5 regulates the asymmetric localization of the LET-99 spindle positioning protein.Dev Biol. 2016 Apr 15;412(2):288-297. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.02.020. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26921457 Free PMC article.
-
Function, dynamics and evolution of network motif modules in integrated gene regulatory networks of worm and plant.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 27;46(13):6480-6503. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky468. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29873777 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

