Protein SRP68 of human signal recognition particle: identification of the RNA and SRP72 binding domains
- PMID: 16672232
- PMCID: PMC2242529
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.051861406
Protein SRP68 of human signal recognition particle: identification of the RNA and SRP72 binding domains
Abstract
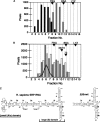
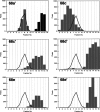
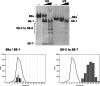
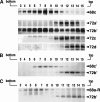
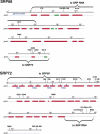
The signal recognition particle (SRP) plays an important role in the delivery of secretory proteins to cellular membranes. Mammalian SRP is composed of six polypeptides among which SRP68 and SRP72 form a heterodimer that has been notoriously difficult to investigate. Human SRP68 was purified from overexpressing Escherichia coli cells and was found to bind to recombinant SRP72 as well as in vitro-transcribed human SRP RNA. Polypeptide fragments covering essentially the entire SRP68 molecule were generated recombinantly or by proteolytic digestion. The RNA binding domain of SRP68 included residues from positions 52 to 252. Ninety-four amino acids near the C terminus of SRP68 mediated the binding to SRP72. The SRP68-SRP72 interaction remained stable at elevated salt concentrations and engaged approximately 150 amino acids from the N-terminal region of SRP72. This portion of SRP72 was located within a predicted tandem array of four tetratricopeptide (TPR)-like motifs suggested to form a superhelical structure with a groove to accommodate the C-terminal region of SRP68.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structures of human SRP72 complexes provide insights into SRP RNA remodeling and ribosome interaction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 9;45(1):470-481. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1124. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899666 Free PMC article.
-
Human apo-SRP72 and SRP68/72 complex structures reveal the molecular basis of protein translocation.J Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 1;9(3):220-230. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjx010. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28369529 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an RNA-binding domain in human SRP72.J Mol Biol. 2005 Jan 28;345(4):659-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.10.087. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15588816
-
Assembly of the 68- and 72-kD proteins of signal recognition particle with 7S RNA.J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(5):977-85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.977. J Cell Biol. 1993. PMID: 8388879 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical Functions and Cellular Dynamics of the Mammalian Signal Recognition Particle Components.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 25;8:679584. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.679584. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34113652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the SRP68/72 interface of human signal recognition particle by systematic site-directed mutagenesis.Protein Sci. 2009 Oct;18(10):2183-95. doi: 10.1002/pro.232. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19693936 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of amino acid residues in protein SRP72 required for binding to a kinked 5e motif of the human signal recognition particle RNA.BMC Mol Biol. 2010 Nov 13;11:83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-83. BMC Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 21073748 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic-Based Machine Learning Analysis Reveals PYGB as a Novel Immunohistochemical Biomarker to Distinguish Inverted Urothelial Papilloma From Low-Grade Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma With Inverted Growth.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 24;12:841398. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.841398. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35402263 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of human SRP72 complexes provide insights into SRP RNA remodeling and ribosome interaction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 9;45(1):470-481. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1124. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899666 Free PMC article.
-
Signal recognition particle: an essential protein-targeting machine.Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:693-721. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-072711-164732. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23414305 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blatch G.L. and Lassle M. 1999. The tetratricopeptide repeat: A structural motif mediating protein–protein interactions Bioessays 21 932–939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

