The crystal structure of human receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase kappa phosphatase domain 1
- PMID: 16672235
- PMCID: PMC2242534
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.062128706
The crystal structure of human receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase kappa phosphatase domain 1
Abstract
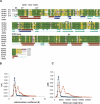
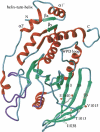
The receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatases (RPTPs) are integral membrane proteins composed of extracellular adhesion molecule-like domains, a single transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. The cytoplasmic domain consists of tandem PTP domains, of which the D1 domain is enzymatically active. RPTPkappa is a member of the R2A/IIb subfamily of RPTPs along with RPTPmu, RPTPrho, and RPTPlambda. Here, we have determined the crystal structure of catalytically active, monomeric D1 domain of RPTPkappa at 1.9 A. Structural comparison with other PTP family members indicates an overall classical PTP architecture of twisted mixed beta-sheets flanked by alpha-helices, in which the catalytically important WPD loop is in an unhindered open conformation. Though the residues forming the dimeric interface in the RPTPmu structure are all conserved, they are not involved in the protein-protein interaction in RPTPkappa. The N-terminal beta-strand, formed by betax association with betay, is conserved only in RPTPs but not in cytosolic PTPs, and this feature is conserved in the RPTPkappa structure forming a beta-strand. Analytical ultracentrifugation studies show that the presence of reducing agents and higher ionic strength are necessary to maintain RPTPkappa as a monomer. In this family the crystal structure of catalytically active RPTPmu D1 was solved as a dimer, but the dimerization was proposed to be a consequence of crystallization since the protein was monomeric in solution. In agreement, we show that RPTPkappa is monomeric in solution and crystal structure.
Figures
References
-
- Alonso A., Sasin J., Bottini N., Friedberg I., Friedberg I., Osterman A., Godzik A., Hunter T., Dixon J., Mustelin T. 2004. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome Cell 117 699–711. - PubMed
-
- Barford D., Flint A.J., Tonks N.K. 1994. Crystal structure of human protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B Science 263 1397–1404. - PubMed
-
- Bilwes A.M., den Hertog J., Hunter T., Noel J.P. 1996. Structural basis for inhibition of receptor protein–tyrosine phosphatase-α by dimerization Nature 382 555–559. - PubMed
-
- Desai D.M., Sap J., Schlessinger J., Weiss A. 1993. Ligand-mediated negative regulation of a chimeric transmembrane receptor tyrosine phosphatase Cell 73 541–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

