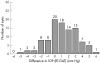Comparison of rebound tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry and correlation with central corneal thickness
- PMID: 16672330
- PMCID: PMC1857178
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2005.089870
Comparison of rebound tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry and correlation with central corneal thickness
Abstract
Background/aims: Rebound tonometry (RT) is performed without anaesthesia with a hand held device. The primary aim was to compare RT with Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT) and to correlate with central corneal thickness (CCT). The secondary aim was to prove tolerability and practicability of RT under "study conditions" and "routine practice conditions."
Methods: In group 1 (52 eyes/28 patients), all measurements were taken by the same physician, in the same room and order: non-contact optical pachymetry, RT, slit lamp inspection, GAT. Patients were questioned about discomfort or pain. In group 2 (49 eyes/27 patients), tonometry was performed by three other physicians during routine examinations.
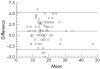
Results: RT was well tolerated and safe. Intraocular pressure (IOP) ranged between 6 mm Hg and 48 mm Hg. No different trends were found between the groups. RT tended to give slightly higher readings: n = 101, mean difference 1.0 (SD 2.17) mm Hg; 84.1% of RT readings within plus or minus 3 mm Hg of GAT; 95% confidence interval in the Bland-Altman analysis -3.2 mm Hg to +5.2 mm Hg. Both RT and GAT showed a weak positive correlation with CCT (r2 0.028 and 0.025, respectively).
Conclusions: RT can be considered a reliable alternative for clinical screening and in cases where positioning of the head at the slit lamp is impossible or topical preparations are to be avoided.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest: none.
References
-
- Goldmann H, Schmidt T H. Über Applanations‐tonometrie. Ophthalmologica 1957134221–242. - PubMed
-
- Kontiola A I. A new electromechanical method for measuring intraocular pressure. Doc Ophthalmol 199793265–276. - PubMed
-
- Kontiola A I. A new induction‐based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 200078142–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical