Epidermal growth factor receptor variant III mutations in lung tumorigenesis and sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 16672372
- PMCID: PMC1456806
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0510284103
Epidermal growth factor receptor variant III mutations in lung tumorigenesis and sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Abstract
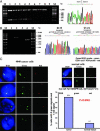
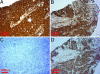
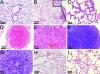
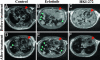
The tyrosine kinase inhibitors gefitinib (Iressa) and erlotinib (Tarceva) have shown anti-tumor activity in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Dramatic and durable responses have occurred in NSCLC tumors with mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). In contrast, these inhibitors have shown limited efficacy in glioblastoma, where a distinct EGFR mutation, the variant III (vIII) in-frame deletion of exons 2-7, is commonly found. In this study, we determined that EGFRvIII mutation was present in 5% (3/56) of analyzed human lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) but was not present in human lung adenocarcinoma (0/123). We analyzed the role of the EGFRvIII mutation in lung tumorigenesis and its response to tyrosine kinase inhibition. Tissue-specific expression of EGFRvIII in the murine lung led to the development of NSCLC. Most importantly, these lung tumors depend on EGFRvIII expression for maintenance. Treatment with an irreversible EGFR inhibitor, HKI-272, dramatically reduced the size of these EGFRvIII-driven murine tumors in 1 week. Similarly, Ba/F3 cells transformed with the EGFRvIII mutant were relatively resistant to gefitinib and erlotinib in vitro but proved sensitive to HKI-272. These findings suggest a therapeutic strategy for cancers harboring the EGFRvIII mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Irreversible inhibitors of the EGF receptor may circumvent acquired resistance to gefitinib.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 24;102(21):7665-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502860102. Epub 2005 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15897464 Free PMC article.
-
The T790M "gatekeeper" mutation in EGFR mediates resistance to low concentrations of an irreversible EGFR inhibitor.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Apr;7(4):874-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2387. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18413800
-
Clinical impact of switching to a second EGFR-TKI after a severe AE related to a first EGFR-TKI in EGFR-mutated NSCLC.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jun;42(6):528-33. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys042. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22457323
-
Chasing targets for EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer: Asian perspectives.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007 Nov;7(6):821-36. doi: 10.1586/14737159.7.6.821. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007. PMID: 18020911 Review.
-
Inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor in combined modality treatment for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Semin Oncol. 2005 Apr;32(2 Suppl 3):S35-41. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.03.008. Semin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16015534 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomics of squamous cell lung cancer.Oncologist. 2013 Jun;18(6):707-16. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0063. Epub 2013 May 31. Oncologist. 2013. PMID: 23728941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic anti-EGFR antibody 806 generates responses in murine de novo EGFR mutant-dependent lung carcinomas.J Clin Invest. 2007 Feb;117(2):346-52. doi: 10.1172/JCI30446. Epub 2007 Jan 25. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17256054 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling oncogene addiction using RNA interference.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Aug 26;105(34):12480-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803217105. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18711136 Free PMC article.
-
Gene silencing for epidermal growth factor receptor variant III induces cell-specific cytotoxicity.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Nov;7(11):3586-97. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0653. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 19001441 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotoxin Therapies for the Treatment of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent Cancers.Toxins (Basel). 2016 May 4;8(5):137. doi: 10.3390/toxins8050137. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27153091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hynes N. E., Lane H. A. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5:341–354. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga C. L. Exp. Cell Res. 2003;284:122–130. - PubMed
-
- Mendelsohn J., Baselga J. Oncogene. 2000;19:6550–6565. - PubMed
-
- Paez J. G., Janne P. A., Lee J. C., Tracy S., Greulich H., Gabriel S., Herman P., Kaye F. J., Lindeman N., Boggon T. J., et al. Science. 2004;304:497–500. - PubMed
-
- Lynch T. J., Bell D. W., Sordella R., Gurubhagavatula S., Okimoto R. A., Brannigan B. W., Harris P. L., Haserlat S. M., Supko J. G., Haluska F. G., et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

