Characterization of the Yersinia enterocolitica type III secretion ATPase YscN and its regulator, YscL
- PMID: 16672607
- PMCID: PMC1482870
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.188.10.3525-3534.2006
Characterization of the Yersinia enterocolitica type III secretion ATPase YscN and its regulator, YscL
Abstract
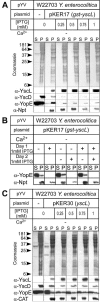
Type III secretion is a mechanism used by a broad range of gram-negative bacteria to neutralize eukaryotic defenses by enabling translocation of bacterial proteins directly into the cytoplasm of host cells. The bacterial energy source for secretion is ATP, which is consumed by an ATPase that couples ATP hydrolysis to the unfolding of secreted proteins and the dissociation of their chaperones just prior to secretion. By studying the biochemical properties of YscN and YscL of Yersinia enterocolitica, we have characterized them as the ATPase and ATPase regulator, respectively, of the type III secretion system of this organism. In vivo, YscL and YscN interact with each other, and the overexpression of glutathione S-transferase-YscL abolishes secretion and down-regulates the expression of secretion apparatus components.
Figures








References
-
- Akeda, Y., and J. E. Galan. 2005. Chaperone release and unfolding of substrates in type III secretion. Nature 437:911-915. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, D. M., and O. Schneewind. 1997. A mRNA signal for the type III secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. Science 278:1140-1143. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, D. M., and O. Schneewind. 1999. Yersinia enterocolitica type III secretion: an mRNA signal that couples translation and secretion of YopQ. Mol. Microbiol. 31:1139-1148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

