Perinatal choline influences brain structure and function
- PMID: 16673755
- PMCID: PMC2438605
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2006.tb00202.x
Perinatal choline influences brain structure and function
Abstract
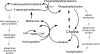
Choline is derived not only from the diet, but also from de novo synthesis. It is important for methyl-group metabolism, the formation of membranes, kidney function, and neurotransmission. When deprived of dietary choline, most adult men and postmenopausal women develop signs of organ dysfunction (fatty liver or muscle damage) and have a decreased capacity to convert homocysteine to methionine. Choline is critical during fetal development, when it influences stem cell proliferation and apoptosis, thereby altering brain structure and function (memory is permanently enhanced in rodents exposed to choline during the latter part of gestation).
Figures
References
-
- Zeisel SH, Blusztajn JK. Choline and human nutrition. Ann Rev. Nutr. 1994;14:269–296. - PubMed
-
- Blusztajn JK, Wurtman RJ. Choline and cholinergic neurons. Science. 1983;221:614–620. - PubMed
-
- Niculescu MD, Zeisel SH. Diet, methyl donors and DNA methylation: interactions between dietary folate, methionine and choline. J Nutr. 2002;132:2333S–2335S. - PubMed
-
- da Costa KA, Badea M, Fischer LM, Zeisel SH. Elevated serum creatine phosphokinase in choline-deficient humans: mechanistic studies in C2C12 mouse myoblasts. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80:163–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

