Endotoxin in inner-city homes: associations with wheeze and eczema in early childhood
- PMID: 16675336
- PMCID: PMC2040050
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.12.1348
Endotoxin in inner-city homes: associations with wheeze and eczema in early childhood
Abstract
Background: An inverse association between domestic exposure to endotoxin and atopy in childhood has been observed. The relevance of this aspect of the hygiene hypothesis to US inner-city communities that have disproportionately high asthma prevalence has not been determined.
Objectives: To measure endotoxin in the dust from inner-city homes, evaluate associations between endotoxin and housing/lifestyle characteristics, and determine whether endotoxin exposure predicted wheeze, allergic rhinitis, and eczema over the first 3 years of life.
Methods: As part of an ongoing prospective birth cohort study, children of Dominican and African-American mothers living in New York City underwent repeated questionnaire measures. Dust samples collected from bedroom floors at age 12 or 36 months were assayed for endotoxin.
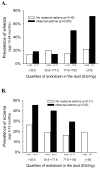
Results: Among the samples collected from 301 participants' homes, the geometric mean endotoxin concentration (95% CI) was 75.9 EU/mg (66-87), and load was 3892 EU/m2 (3351-4522). Lower endotoxin concentrations were associated with wet mop cleaning and certain neighborhoods. Endotoxin concentration correlated weakly with cockroach (Bla g 2: r = 0.22, P < .001) and mouse (mouse urinary protein: r = 0.28; P < .001) allergens in the dust. Children in homes with higher endotoxin concentration were less likely to have eczema at age 1 year (odds ratio, 0.70 [0.53-0.93]) and more likely to wheeze at age 2 years (odds ratio, 1.34 [1.01-1.78]). These associations were stronger among children with a maternal history of asthma.
Conclusion: Endotoxin levels in this inner-city community are similar to those in nonfarm homes elsewhere. In this community, domestic endotoxin exposure was inversely associated with eczema at age 1 year, but positively associated with wheeze at age 2 years.
Clinical implications: Endotoxin exposure in the inner-city community may be related to wheeze in the early life; however, given the inverse association seen with eczema, the long-term development of allergic disease is still in question.
Figures
References
-
- Gereda JE, Leung DY, Thatayatikom A, Streib JE, Price MR, Klinnert MD, et al. Relation between house-dust endotoxin exposure, type 1 T-cell development, and allergen sensitisation in infants at high risk of asthma. Lancet. 2000;355:1680–3. - PubMed
-
- Braun-Fahrlander C, Riedler J, Herz U, Eder W, Waser M, Grize L, et al. Environmental exposure to endotoxin and its relation to asthma in school-age children. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:869–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- M01 RR000645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 ES09600/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011158/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES008977/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES05605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 ES009600/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 5 R01 ES08977/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES009089/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES111158/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES009600/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- RR00645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES012468/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 5 P30 ES009089/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials