Luteinizing hormone-induced RUNX1 regulates the expression of genes in granulosa cells of rat periovulatory follicles
- PMID: 16675540
- PMCID: PMC1783681
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2005-0512
Luteinizing hormone-induced RUNX1 regulates the expression of genes in granulosa cells of rat periovulatory follicles
Abstract
The LH surge induces specific transcription factors that regulate the expression of a myriad of genes in periovulatory follicles to bring about ovulation and luteinization. The present study determined 1) the localization of RUNX1, a nuclear transcription factor, 2) regulation of Runx1 mRNA expression, and 3) its potential function in rat ovaries. Up-regulation of mRNA and protein for RUNX1 is detected in preovulatory follicles after human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) injection in gonadotropin-treated immature rats as well as after the LH surge in cycling animals by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemical and Western blot analyses. The regulation of Runx1 mRNA expression was investigated in vitro using granulosa cells from rat preovulatory ovaries. Treatments with hCG, forskolin, or phorbol 12 myristate 13-acetate stimulated Runx1 mRNA expression. The effects of hCG were reduced by inhibitors of protein kinase A, MAPK kinase, or p38 kinase, indicating that Runx1 expression is regulated by the LH-initiated activation of these signaling mediators. In addition, hCG-induced Runx1 mRNA expression was inhibited by a progesterone receptor antagonist and an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, whereas amphiregulin stimulated Runx1 mRNA expression, demonstrating that the expression is mediated by the activation of the progesterone receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor. Finally, knockdown of Runx1 mRNA by small interfering RNA decreased progesterone secretion and reduced levels of mRNA for Cyp11a1, Hapln1, Mt1a, and Rgc32. The hormonally regulated expression of Runx1 in periovulatory follicles, its involvement in progesterone production, and regulation of preovulatory gene expression suggest important roles of RUNX1 in the periovulatory process.
Figures




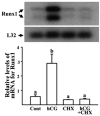
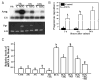



References
-
- Espey LL, Richards JS. Temporal and spatial patterns of ovarian gene transcription following an ovulatory dose of gonadotropin in the rat. Biol Reprod. 2002;67:1662–1670. - PubMed
-
- Richards JS, Russell DL, Ochsner S, Espey LL. Ovulation: new dimensions and new regulators of the inflammatory-like response. Annu Rev Physiol. 2002;64:69–92. - PubMed
-
- Richards JS. Ovulation: new factors that prepare the oocyte for fertilization. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005;234:75–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

