The macrophage scavenger receptor SR-AI/II and lung defense against pneumococci and particles
- PMID: 16675784
- PMCID: PMC2643266
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0128OC
The macrophage scavenger receptor SR-AI/II and lung defense against pneumococci and particles
Abstract
The class A macrophage scavenger receptor SR-AI/II is implicated as a pattern recognition receptor for innate immunity, but its functional role in lung defense has not been studied. We used mice genetically deficient in SR-AI/II and their wild-type C57BL/6 counterparts to investigate the contribution of this receptor to defense against pneumococcal infection and inhaled particles. SR-AI/II deficiency caused impaired phagocytosis of fluorescent bacteria in vivo, diminished clearance of live bacteria from the lungs, and substantially increased pneumonic inflammation. Survival studies also showed increased mortality in SR-AI/II-deficient mice with pneumococcal lung infection. Similarly, after challenge of the airways with TiO(2) particles, SR-AI/II-deficient mice showed increased proinflammatory cytokine levels in lung lavage fluid and a more pronounced neutrophilic inflammation. The data indicate that the lung macrophage class A scavenger receptor SR-AI/II contributes to innate defense against bacteria and inhaled particles.
Figures


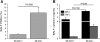


References
-
- Platt N, Haworth R, Darley L, Gordon S. The many roles of the class A macrophage scavenger receptor. Int Rev Cytol 2002;212:1–40. - PubMed
-
- Arredouani M, Kobzik L. The structure and function of Marco, a macrophage class a scavenger receptor. Cell Mol Biol 2004;OL657–OL665. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura K, Funakoshi H, Tokunaga F, Nakamura T. Molecular cloning of a mouse scavenger receptor with C-type lectin (SRCL)(1), a novel member of the scavenger receptor family. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001;1522:53–58. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Oliver P, Davies KE, Platt N. Identification and characterisation of murine SCARA5, a novel class A scavenger receptor that is expressed by populations of epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2006;281: 11834–11845. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki H, Kurihara Y, Takeya M, Kamada N, Kataoka M, Jishage K, Sakaguchi H, Kruijt JK, Higashi T, Suzuki T, et al. The multiple roles of macrophage scavenger receptors (MSR) in vivo: resistance to atherosclerosis and susceptibility to infection in MSR knockout mice. J Atheroscler Thromb 1997;4:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

