Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: controller of systemic inflammation
- PMID: 16677407
- PMCID: PMC1550887
- DOI: 10.1186/cc4899
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: controller of systemic inflammation
Abstract
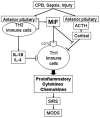
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a cytokine that is secreted by the anterior pituitary and immune cells in response to surgical stress, injury, and sepsis. This cytokine appears to be a critical regulator of the inflammatory pathways, leading to systemic inflammatory response syndrome and subsequent multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. This report provides an integrated scheme describing the manner by which MIF controls the neurohormonal response and the adaptive immune system, namely the T-helper (Th)1 and Th2 lymphocytes, which results in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10. The development of systemic inflammatory response syndrome and subsequent development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome appear to be related to MIF levels and the balance of Th1 and Th2 function.
Figures
Comment on
-
Circulating inflammatory mediators and organ dysfunction after cardiovascular surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a prospective observational study.Crit Care. 2006;10(2):R46. doi: 10.1186/cc4857. Crit Care. 2006. PMID: 16542504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Mendoça-Filho HTF, Pereira KC, Fontes M, Vieira DASA, de Mendonça MLAF, Campos LAA, Castro-Faria-Neto HC. Circulating inflammatory mediators and organ dysfunction after cardiovascular surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a prospective observational study. Crit Care. 2006;10:R46. doi: 10.1186/cc4857. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rogge L. A genomic view of helper T cell subsets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;975:57–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous