Targeted cardiac expression of soluble Fas prevents the development of heart failure in mice with cardiac-specific expression of MCP-1
- PMID: 16678847
- PMCID: PMC1523423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2006.03.010
Targeted cardiac expression of soluble Fas prevents the development of heart failure in mice with cardiac-specific expression of MCP-1
Abstract
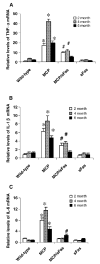
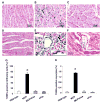
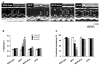
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) plays a crucial role in initiating coronary heart disease by recruiting monocytes/macrophages to the vessel wall. Transgenic mice with cardiac-specific expression of MCP-1 manifest cardiac inflammation and develop heart failure. The pathways mediating the detrimental effects of MCP-1 expression have not been defined. We postulate that the Fas ligand (FasL) derived from the infiltrating mononuclear cells causes death of cardiac cells resulting in the development of heart failure. Here, we tested this hypothesis by determining whether inhibition of FasL function through cardiac-specific expression of soluble Fas (sFas) would rescue the MCP-1 transgenic mice from developing heart failure. We generated mice with cardiac-specific expression of sFas and double homozygous transgenic mice that express both MCP-1 and sFas. Cardiac-specific expression of sFas in MCP mice, in fact, inhibited apoptosis of infiltrating mononuclear cells, normalized circulating C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and prevented macrophage activation as well as production of proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1beta, and IL-6 in the hearts. sFas expression resulted in restoration of cardiac structure, preservation of cardiac function, and a significant prolongation of survival of MCP mice. These results demonstrate that FasL released from infiltrating mononuclear cells plays a critical role in the detrimental effects of MCP-1 expression, and suggest that Fas/FasL signaling represents a novel therapeutic target for heart failure.
Figures

References
-
- Ikeda U. Inflammation and coronary artery disease. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2003;1:65–70. - PubMed
-
- De Lemons JA, Morrow DA, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Gibson GM, Antman EM, et al. Association between plasma levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and long-term clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Circulation. 2003;107:690–5. - PubMed
-
- Deo R, Khera A, McGuire DK, Murphy SA, Meo Neto Jde P, Morrow DA, et al. Association among plasma levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and subclinical atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:1792–800. - PubMed
-
- Sheikine Y, Hansson GK. Chemokines and atherosclerosis. Ann Med. 2004;36:98–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

