Nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-2 is the ecto-ATPase of type I cells in taste buds
- PMID: 16680780
- PMCID: PMC2212711
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.20954
Nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-2 is the ecto-ATPase of type I cells in taste buds
Abstract
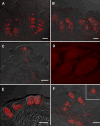
The presence of one or more calcium-dependent ecto-ATPases (enzymes that hydrolyze extracellular 5'-triphosphates) in mammalian taste buds was first shown histochemically. Recent studies have established that dominant ecto-ATPases consist of enzymes now called nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolases (NTPDases). Massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) from murine taste epithelium provided molecular evidence suggesting that NTPDase2 is the most likely member present in mouse taste papillae. Immunocytochemical and enzyme histochemical staining verified the presence of NTPDase2 associated with plasma membranes in a large number of cells within all mouse taste buds. To determine which of the three taste cell types expresses this enzyme, double-label assays were performed with antisera directed against the glial glutamate/aspartate transporter (GLAST), the transduction pathway proteins phospholipase Cbeta2 (PLCbeta2) or the G-protein subunit alpha-gustducin, and serotonin (5HT) as markers of type I, II, and III taste cells, respectively. Analysis of the double-labeled sections indicates that NTPDase2 immunoreactivity is found on cell processes that often envelop other taste cells, reminiscent of type I cells. In agreement with this observation, NTPDase2 was located to the same membrane as GLAST, indicating that this enzyme is present in type I cells. The presence of ecto-ATPase in taste buds likely reflects the importance of ATP as an intercellular signaling molecule in this system.
Copyright 2006 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G. Purinergic signaling-pathophysiological roles. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1998;78:113–145. - PubMed
-
- Adler E, Hoon MA, Mueller KL, Chandrashekar J, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS. A novel family of mammalian taste receptors. Cell. 2000;100:693–702. - PubMed
-
- Akisaka T, Oda M. The fine structural localization of adenosine triphosphatase activity on the taste bud in the fungiform papillae of the rat. Arch Histol Jpn. 1977;40:63. - PubMed
-
- Barry M. Ecto-calcium-dependent ATPase activity of mammalian taste buds cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992;40:1919–1928. - PubMed
-
- Baryshnikov SG, Rogachevskaja OA, Kolesnikov SS. Calcium signaling mediated by P2Y receptors in mouse taste cells. J Neurophysiol. 2003;90:3283–3294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

