Evolution of two alanine glyoxylate aminotransferases in mosquito
- PMID: 16681462
- PMCID: PMC1533304
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060469
Evolution of two alanine glyoxylate aminotransferases in mosquito
Abstract
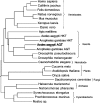
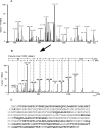
In the mosquito, transamination of 3-HK (3-hydroxykynurenine) to XA (xanthurenic acid) is catalysed by an AGT (alanine glyoxylate aminotransferase) and is the major branch pathway of tryptophan metabolism. Interestingly, malaria parasites hijack this pathway to use XA as a chemical signal for development in the mosquito. Here, we report that the mosquito has two AGT isoenzymes. One is the previously cloned AeHKT [Aedes aegypti HKT (3-HK transaminase)] [Han, Fang and Li (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 15781-15787], similar to hAGT (human AGT), which primarily catalyses 3-HK to XA in mosquitoes, and the other is a typical dipteran insect AGT. We cloned the second AGT from Ae. aegypti mosquitoes [AeAGT (Ae. aegypti AGT)], overexpressed the enzyme in baculovirus/insect cells and determined its biochemical characteristics. We also expressed hAGT for a comparative study. The new cloned AeAGT is highly substrate-specific when compared with hAGT and the previously reported AeHKT and Drosophila AGT, and is translated mainly in pupae and adults, which contrasts with AeHKT that is expressed primarily in larvae. Our results suggest that the physiological requirements of mosquitoes and the interaction between the mosquito and its host appear to be the driving force in mosquito AGT evolution.
Figures


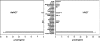

Similar articles
-
Comparative characterization of Aedes 3-hydroxykynurenine transaminase/alanine glyoxylate transaminase and Drosophila serine pyruvate aminotransferase.FEBS Lett. 2002 Sep 11;527(1-3):199-204. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03229-5. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12220660 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of Aedes aegypti alanine glyoxylate aminotransferase.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 1;281(48):37175-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607032200. Epub 2006 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16990263
-
3-Hydroxykynurenine transaminase identity with alanine glyoxylate transaminase. A probable detoxification protein in Aedes aegypti.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 3;277(18):15781-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201202200. Epub 2002 Mar 5. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11880382
-
Alanine glyoxylate aminotransferase deficiency: biochemical and molecular genetic lessons from the study of a human disease.Adv Enzyme Regul. 1992;32:309-27. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(92)90024-t. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1992. PMID: 1496924 Review.
-
Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 and peroxisome-to-mitochondrion mistargeting of alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase.Biochimie. 1993;75(3-4):309-15. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90091-6. Biochimie. 1993. PMID: 8507692 Review.
Cited by
-
The tryptophan oxidation pathway in mosquitoes with emphasis on xanthurenic acid biosynthesis.J Insect Physiol. 2007 Mar;53(3):254-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2006.09.004. Epub 2006 Sep 17. J Insect Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17070835 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Evolution of a Potent Target of Mosquito Larvicide, 3-Hydroxykynurenine Transaminase.Molecules. 2022 Aug 2;27(15):4929. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154929. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956879 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of 3-Hydroxykynurenine Transaminase from Aedes aegypti and Anopheles gambiae: A Mosquito-Specific Target to Combat the Transmission of Arboviruses.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2023 Feb 16;3(2):211-222. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.2c00080. eCollection 2023 Apr 19. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2023. PMID: 37101811 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling forensic timelines using molecular markers in Phormia regina maggots.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 7:2025.04.30.651557. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.30.651557. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654918 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A second generation of 1,2,4-oxadiazole derivatives with enhanced solubility for inhibition of 3-hydroxykynurenine transaminase (HKT) from Aedes aegypti.RSC Med Chem. 2020 Dec 9;12(2):222-236. doi: 10.1039/d0md00305k. eCollection 2021 Mar 4. RSC Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 34046611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J., Li G. Transamination of 3-hydroxykynurenine to produce xanthurenic acid: a major branch pathway of tryptophan metabolism in the mosquito, Aedes aegypti, during larval development. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997;27:859–867. - PubMed
-
- Han Q., Fang J., Li J. 3-Hydroxykynurenine transaminase identity with alanine glyoxylate transaminase. A probable detoxification protein in Aedes aegypti. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:15781–15787. - PubMed
-
- Garcia G. E., Wirtz R. A., Barr J. R., Woolfitt A., Rosenberg R. Xanthurenic acid induces gametogenesis in Plasmodium, the malaria parasite. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:12003–12005. - PubMed
-
- Billker O., Dechamps S., Tewari R., Wenig G., Franke-Fayard B., Brinkmann V. Calcium and a calcium-dependent protein kinase regulate gamete formation and mosquito transmission in a malaria parasite. Cell. 2004;117:503–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

