Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of human phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1 (PRS1)
- PMID: 16682768
- PMCID: PMC2219982
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309106009067
Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of human phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1 (PRS1)
Abstract
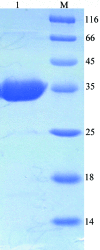
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase (PRS; EC 2.7.6.1) catalyzes the reaction of ribose-5-phosphate (R5P) with ATP to yield AMP and PRPP (5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate), which is necessary for the de novo and salvage pathways of purine-, pyrimidine- and pyridine-nucleotide biosynthesis. PRPP is a metabolite that is required at all times in the cell and is thus central to life. In this study, human PRS1 was produced in Escherichia coli in soluble form and purified to homogeneity. Crystals in complex with Mg2+, inorganic phosphate (P(i)) and ATP were obtained by the hanging-drop vapour-diffusion method. Diffraction data were collected to 2.6 A resolution. The crystal belongs to space group R3, with unit-cell parameters a = b = 168.846, c = 61.857 angstroms, assuming two molecules in the asymmetric unit and a volume-to-weight ratio of 2.4 angstroms3 Da(-1), which was consistent with the result calculated from the self-rotation function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structures of Thermoplasma volcanium phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase bound to ribose-5-phosphate and ATP analogs.J Mol Biol. 2011 Nov 4;413(4):844-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.09.007. Epub 2011 Sep 21. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21963988
-
Overexpression of Bacillus subtilis phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase and crystallization and preliminary X-ray characterization of the free enzyme and its substrate-effector complexes.Proteins. 1996 Feb;24(2):238-46. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(199602)24:2<238::AID-PROT10>3.0.CO;2-O. Proteins. 1996. PMID: 8820490
-
Purine biosynthesis de novo in bovine retina: purification and characterization of amidophosphoribosyl transferase and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase.Biochemistry (Mosc). 1999 Jun;64(6):648-51. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1999. PMID: 10395979
-
[PRPP synthetase superactivity].Nihon Rinsho. 1996 Dec;54(12):3309-14. Nihon Rinsho. 1996. PMID: 8976111 Review. Japanese.
-
Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase and the regulation of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate production in human cells.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;69:115-48. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)69046-9. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11550793 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations in PRPS1 causing syndromic or nonsyndromic hearing impairment: intrafamilial phenotypic variation complicates genetic counseling.Pediatr Res. 2015 Jul;78(1):97-102. doi: 10.1038/pr.2015.56. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Pediatr Res. 2015. PMID: 25785835
-
Contribution of Model Organisms to Investigating the Far-Reaching Consequences of PRPP Metabolism on Human Health and Well-Being.Cells. 2022 Jun 13;11(12):1909. doi: 10.3390/cells11121909. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRPS2 mutations drive acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapse through influencing PRPS1/2 hexamer stability.Blood Sci. 2022 Nov 4;5(1):39-50. doi: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000139. eCollection 2023 Jan. Blood Sci. 2022. PMID: 36742181 Free PMC article.
-
Negative feedback-defective PRPS1 mutants drive thiopurine resistance in relapsed childhood ALL.Nat Med. 2015 Jun;21(6):563-71. doi: 10.1038/nm.3840. Epub 2015 May 11. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25962120 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoribosyl Diphosphate (PRPP): Biosynthesis, Enzymology, Utilization, and Metabolic Significance.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Dec 28;81(1):e00040-16. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-16. Print 2017 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 28031352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Becker, M. A. (2005). Phosphoribosyl Pyrophosphate Synthetase Superactivity. http://www.orpha.net/data/patho/GB/uk-prpp.pdf.
-
- Becker, M. A., Heidler, S. A., Bell, G. I., Seino, S., LeBeau, M. M., Westbrook, C. A., Neuman, W., Shapiro, L. J., Mohandas, T. K. & Roessler, B. J. (1990). Genomics, 8, 550–561. - PubMed
-
- Becker, M. A., Taylor, W., Smith, P. R. & Ahmed, M. (1996). J. Biol. Chem.271, 19894–19899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous