The clinical applications of a systems approach
- PMID: 16683861
- PMCID: PMC1459481
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030209
The clinical applications of a systems approach
Abstract
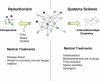
In the second of a two part series, Ahn and colleagues provide a practical discussion of how a systems approach will affect clinical medicine, using diabetes as an example.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Toni R, Malaguti A, Castorina S, Roti E, Lechan RM. New paradigms in neuroendocrinology: Relationships between obesity, systemic inflammation and the neuroendocrine system. J Endocrinol Invest. 2004;27:182–186. - PubMed
-
- Crook M. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A disease of the innate immune system? An update. Diabet Med. 2004;21:203–207. - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil G. Inflammatory pathways and insulin action. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27(Suppl 3):53–55. - PubMed
-
- Shoelson SE, Lee J, Yuan M. Inflammation and the IKK beta/I kappa B/ NF-kappa B axis in obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27(Suppl 3):49–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

