The emerging strains of Shigella dysenteriae type 2 in Bangladesh are clonal
- PMID: 16684401
- PMCID: PMC2870502
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268806006029
The emerging strains of Shigella dysenteriae type 2 in Bangladesh are clonal
Abstract
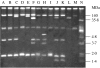
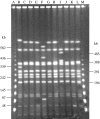
A total of 113 strains of Shigella dysenteriae type 2 isolated from patients attending the Dhaka diarrhoea treatment centre of ICDDR,B: Centre for Health and Population Research during the period 1999-2004 were studied. Serotype of the isolates was confirmed using commercially available antisera. Except for arabinose fermentation, all the strains had similar biochemical reactions. More than 60% of the strains were sensitive to commonly used antibiotics; only 6% (n=7) of the strains were resistant to nalidixic acid, and none of the strains were resistant to mecillinam and ciprofloxacin. All strains were invasive as demonstrated by the presence of a 140 MDa plasmid, ial, sen and ipaH genes, Congo Red absorption ability and by the Sereny test performed on representative strains. Plasmid patterns were heterogeneous but more than 50% of strains were confined to a single pattern. All strains possessed a 1.6 MDa plasmid and 87% of the strains contained a 4 MDa plasmid. Middle-range plasmids (90 MDa to 30 MDa) present in 36% of the strains were not associated with antibiotic resistance. All the strains were clustered within a single type with four subtypes by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis while ribotyping patterns of all the strains were identical.
Figures
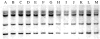
Similar articles
-
Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of provisional serotype Shigella flexneri 1c and clonal relationships with 1a and 1b strains isolated in Bangladesh.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Jan;41(1):110-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.1.110-117.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12517835 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of serologically atypical strains of Shigella flexneri type 4 isolated in Dhaka, Bangladesh.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Jul;40(7):2490-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.7.2490-2497.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12089268 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a serologically atypical Shigella flexneri Z isolated from diarrheal patients in Bangladesh and a proposed serological scheme for Shigella flexneri.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 24;13(8):e0202704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202704. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30142163 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of serologically atypical provisional serovars of Shigella isolates from Kolkata, India.J Med Microbiol. 2014 Dec;63(Pt 12):1696-1703. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.081307-0. Epub 2014 Sep 26. J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25261061
-
A novel serovar of Shigella dysenteriae from patients with diarrhoea in Bangladesh.J Med Microbiol. 2007 May;56(Pt 5):654-658. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46999-0. J Med Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17446289
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of the genomes of Shigella dysenteriae type 2 & type 7 isolates.Indian J Med Res. 2013 Jan;137(1):169-77. Indian J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 23481068 Free PMC article.
-
Changing trends in the prevalence of Shigella species: emergence of multi-drug resistant Shigella sonnei biotype g in Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 18;8(12):e82601. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082601. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24367527 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors and outcome of Shigella encephalopathy in Bangladeshi children.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Apr 28;11(4):e0005561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005561. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 28453565 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the vaccine potential of an in silico designed FepA peptide vaccine against Shigella flexneri in mice model.Vaccine X. 2024 May 8;18:100493. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2024.100493. eCollection 2024 Jun. Vaccine X. 2024. PMID: 38812954 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Antibiotic-Resistant Shigella spp. in Bangladesh: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 44,519 Samples.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 26;12(5):817. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12050817. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Mortality by cause for eight reasons of the world: global burden of disease study. Lancet. 1997;349:1269–1276. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Global mortality, disability, and the contribution of risk factors: global burden of disease study. Lancet. 1997;349:1436–1442. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi S et al. Growing antimicrobial resistance of Shigella isolates. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2003;512:427–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

