The biological actions of dehydroepiandrosterone involves multiple receptors
- PMID: 16684650
- PMCID: PMC2423429
- DOI: 10.1080/03602530600569877
The biological actions of dehydroepiandrosterone involves multiple receptors
Abstract
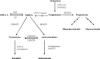
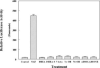
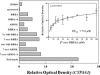
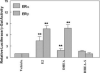
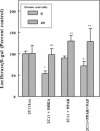
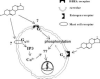
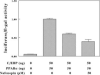
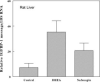
Dehydroepiandrosterone has been thought to have physiological functions other than as an androgen precursor. The previous studies performed have demonstrated a number of biological effects in rodents, such as amelioration of disease in diabetic, chemical carcinogenesis, and obesity models. To date, activation of the peroxisome proliferators activated receptor alpha, pregnane X receptor, and estrogen receptor by DHEA and its metabolites have been demonstrated. Several membrane-associated receptors have also been elucidated leading to additional mechanisms by which DHEA may exert its biological effects. This review will provide an overview of the receptor multiplicity involved in the biological activity of this sterol.
Figures
References
-
- Abuissa H, Bel DS, O'Keefe JH., Jr. Strategies to prevent type 2 diabetes. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2005;21:1107–1114. - PubMed
-
- Allolio B, Arlt W. DHEA treatment: myth or reality? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002;13:288–294. - PubMed
-
- Apostolova G, Schweizer RA, Balazs Z, Kostadinova RM, Odermatt A. Dehydroepiandrosterone inhibits the amplification of glucocorticoid action in adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005;288:E957–E964. - PubMed
-
- Arad Y, Badimon JJ, Badimon L, Hembree WC, Ginsberg HN. Dehydroepiandrosterone feeding prevents aortic fatty streak formation and cholesterol accumulation in cholesterol-fed rabbit. Arteriosclerosis. 1989;9:159–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
