Mutant POLG2 disrupts DNA polymerase gamma subunits and causes progressive external ophthalmoplegia
- PMID: 16685652
- PMCID: PMC1474082
- DOI: 10.1086/504303
Mutant POLG2 disrupts DNA polymerase gamma subunits and causes progressive external ophthalmoplegia
Abstract
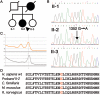
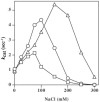
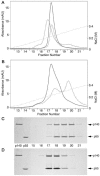
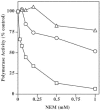
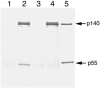
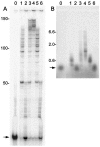
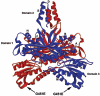
DNA polymerase gamma (pol gamma ) is required to maintain the genetic integrity of the 16,569-bp human mitochondrial genome (mtDNA). Mutation of the nuclear gene for the catalytic subunit of pol gamma (POLG) has been linked to a wide range of mitochondrial diseases involving mutation, deletion, and depletion of mtDNA. We describe a heterozygous dominant mutation (c.1352G-->A/p.G451E) in POLG2, the gene encoding the p55 accessory subunit of pol gamma , that causes progressive external ophthalmoplegia with multiple mtDNA deletions and cytochrome c oxidase (COX)-deficient muscle fibers. Biochemical characterization of purified, recombinant G451E-substituted p55 protein in vitro revealed incomplete stimulation of the catalytic subunit due to compromised subunit interaction. Although G451E p55 retains a wild-type ability to bind DNA, it fails to enhance the DNA-binding strength of the p140-p55 complex. In vivo, the disease most likely arises through haplotype insufficiency or heterodimerization of the mutated and wild-type proteins, which promote mtDNA deletions by stalling the DNA replication fork. The progressive accumulation of mtDNA deletions causes COX deficiency in muscle fibers and results in the clinical phenotype.
Figures

References
Web Resources
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for POLG2 [accession number NM_007215])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for PEOA1, PEOB, Alpers syndrome, and ataxia with peripheral neuropathy)
References
-
- Lamantea E, Tiranti V, Bordoni A, Toscano A, Bono F, Servidei S, Papadimitriou A, Spelbrink H, Silvestri L, Casari G, Comi G, Zeviani M (2002) Mutations of mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ are a frequent cause of autosomal dominant or recessive progressive external ophthalmoplegia. Ann Neurol 52:211–219 10.1002/ana.10278 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

