Cross-species hybridizations on a multi-species cDNA microarray to identify evolutionarily conserved genes expressed in oocytes
- PMID: 16686947
- PMCID: PMC1475851
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-113
Cross-species hybridizations on a multi-species cDNA microarray to identify evolutionarily conserved genes expressed in oocytes
Abstract
Background: Comparative genomic analysis using cDNA microarray is a new approach and a useful tool to identify important genetic sequences or genes that are conserved throughout evolution. Identification of these conserved sequences will help elucidate important molecular mechanisms or pathways common to many species. For example, the stockpiled transcripts in the oocyte necessary for successful fertilization and early embryonic development still remain relatively unknown. The objective of this study was to identify genes expressed in oocytes and conserved in three evolutionarily distant species.
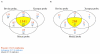
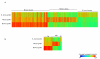
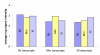
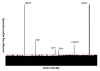
Results: In this study we report the construction of a multi-species cDNA microarray containing 3,456 transcripts from three distinct oocyte-libraries from bovine, mouse and Xenopus laevis. Following the cross-species hybridizations, data analysis revealed that 1,541 positive hybridization signals were generated by oocytes of all three species, and 268 of these are preferentially expressed in the oocyte. Data reproducibility analyses comparing same-species to cross-species hybridization indicates that cross-species hybridizations are highly reproducible, thus increasing the confidence level in their specificity. A validation by RT-PCR using gene- and species-specific primers confirmed that cross-species hybridization allows the production of specific and reliable data. Finally, a second validation step through gene-specific microarray hybridizations further supported the validity of our cross-species microarray results. Results from these cross-species hybridizations on our multi-species cDNA microarray revealed that SMFN (Small fragment nuclease), Spin (Spindlin), and PRMT1 (Protein arginine methyltransferase 1) are transcripts present in oocytes and conserved in three evolutionarily distant species.
Conclusion: Cross-species hybridization using a multi-species cDNA microarray is a powerful tool for the discovery of genes involved in evolutionarily conserved molecular mechanisms. The present study identified conserved genes in the oocytes of three distant species that will help understand the unique role of maternal transcripts in early embryonic development.
Figures
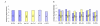
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of oocyte transcript profiles reveals a high degree of conservation among species.Reproduction. 2008 Apr;135(4):439-48. doi: 10.1530/REP-07-0342. Reproduction. 2008. PMID: 18367505
-
Cross-species hybridisation of human and bovine orthologous genes on high density cDNA microarrays.BMC Genomics. 2004 Oct 28;5:83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-83. BMC Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15511299 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel and known oocyte-specific genes using complementary DNA subtraction and microarray analysis in three different species.Biol Reprod. 2005 Jul;73(1):63-71. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.037069. Epub 2005 Mar 2. Biol Reprod. 2005. PMID: 15744023
-
Cross-species microarray hybridizations: a developing tool for studying species diversity.Trends Genet. 2007 Apr;23(4):200-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2007.02.003. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Trends Genet. 2007. PMID: 17313995 Review.
-
Genomic profiling: cDNA arrays and oligoarrays.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;823:89-105. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-216-2_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22081341 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcript profiling of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) using the GeneChip Soybean Genome Array: optimizing analysis by masking biased probes.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 May 7;10:85. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-85. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20459672 Free PMC article.
-
Application of chicken microarrays for gene expression analysis in other avian species.BMC Genomics. 2009 Jul 14;10 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-S2-S3. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19607654 Free PMC article.
-
Large scale comparison of global gene expression patterns in human and mouse.Genome Biol. 2010;11(12):R124. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r124. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 21182765 Free PMC article.
-
Novel functions of protein arginine methyltransferase 1 in thyroid hormone receptor-mediated transcription and in the regulation of metamorphic rate in Xenopus laevis.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;29(3):745-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00827-08. Epub 2008 Dec 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19047371 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression during the oocyte-to-embryo transition in mammals.Mol Reprod Dev. 2009 Sep;76(9):805-18. doi: 10.1002/mrd.21038. Mol Reprod Dev. 2009. PMID: 19363788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

